Thiamine bromide (vitamin B1 (aneurine, betiamine, betavitan,Vetanevrin). Also released Thiamine chloride. White or yellowish crystalline powder. Easily destroyed in alkaline and neutral solutions. When interacting with other substances containing sulfhydryl groups, they easily form dithio compounds.
Contained in cereals, karmas of plant and animal origin.
Thiamine itself has low biological activity, but after absorption from the intestine, it is rapidly phosphorylated and converted into thiamine pyrophosphate, which is a coenzyme of decarboxylases. Thiamine phosphates carry out oxidative and non-oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid. With a lack of vitamin B1, pyruvic acid accumulates in the blood, tissues, brain, causing toxicosis, nervous disorders, and polyneuritis.
Taking part in the process of carboxylation and decarboxylation of pyruvic acid, thiamine affects the synthesis of glycogen from glucose, the conversion of fructose into glucose, and the synthesis of carbohydrates from lactic and pyruvic acids. It enhances the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and the hyperglycemic effect of glucose. It affects nitrogen metabolism by regulating transamination in amino acid metabolism, accelerates the synthesis of glutamine in the liver and brain, and has a positive effect on nucleotide metabolism. In addition, thiamine activates choline acetylase and blocks cholinesterase, increasing the level of acetylcholine in the body, thereby affecting the function of cholinergic nerves.
With hypovitaminosis of thiamine, carbohydrate and water-salt metabolism is disturbed. The synthesis of acetylcholine decreases, and paresis, paralysis of skeletal muscles, intestinal atony occur. The synthesis of trypsin, amylase, lipase is inhibited, and, consequently, the digestion and assimilation of feed (dyspeptic phenomena), and, as a result, the growth and development of young animals are delayed, malnutrition develops, and heart failure often occurs.
Thiamine antagonists: oxythiamine, pyrithiamin and other substances formed in violation of thiamine transformations. They not only prevent the manifestation of the action of thiamine, but also lead to the appearance of toxic decomposition products of the vitamin that disrupt metabolism. Thiamine is incompatible with rodergam, tannin, strychnine, quinine, adrenolytic and sympatholytic substances, penicillin, streptomycin, hypnotics, folic and nicotinic acids, ftivazid and prozerin. Thiamine enhances and lengthens the hypotensive effect of papaverine, accelerates and lengthens the pharmacological action of cardiac glycosides. In some feeds and poisonous plants (horsetail, fern), intestinal bacteria have thiaminase - an enzyme that breaks down thiamine.
It is used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes in B1-hypovitaminosis, lowering the tone of the uterus during childbirth, lowering the tone of capillaries, with a neurotoxic form of dyspepsia in suckling pigs, dyspepsia in calves, as well as in pneumonia with a tendency to swelling, gastritis and enteritis with symptoms atony.
Dry brewer's yeast. They contain vitamin B1 (14 mg%) and B2 (3 mg%), as well as proteins and other substances.
Tablets "Gefefitin". They contain dry beer yeast (0.375 g) and phytin (0.125 g).
Solution "Tiodinzh Contains 12.5 mg of thiamine bromide and 10 mg of sodium iodide in 1 ml. Colorless transparent liquid with a slight specific odor.
Phosphotiamine. 4-Methyl-5-p-hydroxyethyl-7U-(2"-methyl-4"-amino-5"-methylpyrimidyl)-thiazolium phosphate. Monophosphoric ether. White crystalline powder, sour taste. Easily soluble in water. The drug according to the main pharmacological properties does not differ from other synthetic vitamin preparations IN. It is more deposited in the tissues of the body, is destroyed to a lesser extent by the enzyme thiaminase, more easily passes into cocarboxylase, and is less toxic.
Applied in the same cases as the vitamin IN 1.
Store in a place protected from light.
Cocarboxylase (thiamine pyrophosphate, catiamin, etc.). Thiamine diphosphoric ester. By biological action it approaches vitamins and enzymes. Thiamine introduced into the body is phosphorylated and converted into cocarboxylase. The biological properties of cocarboxylase do not fully coincide with the properties of thiamine, so it is ineffective in B1-hypovitaminosis.
It is used for acidosis arising from metabolic disorders (carbohydrate and protein), intoxication, liver and kidney failure, weakening of cardiac activity.
Benfotiamine. 2-Methyl-4-amino-5-(1"-phosphate-3"-benzoylthio-4"-methylbut-3"-ene-4"-formamidomethyl)-pyrimidine. White crystalline powder with a slight characteristic odor. Insoluble in water When taken orally, it is well absorbed.
It is used for B1-hypovitaminosis, functional disorders from the central nervous system, gastrointestinal diseases (dyspepsia in newborn animals).
Riboflavin (vitaminAT 2)(beflavin, lactoflavin, Vitaflavin And etc.). 6,7-Dimethyl-9-(D-1-ribityl)-isoalloxazine. Yellow-orange crystalline powder with a bitter taste. Slightly soluble in water. It contains ribose. Widely distributed in flora and fauna. Obtained synthetically. Bacterial biosynthesis is carried out in the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, however, the intensity of this synthesis depends on the composition of the diets.
Absorbed from the intestine, riboflavin with the participation of ATP is phosphorylated and converted into flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. Both coenzymes take part in redox processes as part of dehydrogenases and oxidases. The group of enzymes that contain riboflavin is called flavin enzymes.
Riboflavin is involved in the processes of carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism, in the synthesis of hemoglobin, in the formation of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice, increases the content of free hydrochloric acid in hypo- and anacid gastritis. With a lack of it, the exchange is disturbed ascorbic acid(its deficiency occurs), and with a lack of ascorbic acid, the need for riboflavin increases. With a deficiency of thiamine, the effect of riboflavin weakens, and with total absence its riboflavin in feed loses its vitamin properties.
More than 95% of riboflavin in tissues is contained in a bound form, which is regulated by the nervous system. Riboflavin is essential for proper absorption, assimilation and synthesis of fat. Lack of it in the diet is accompanied by violations of the processes of use nutrients- carbohydrates, proteins, the development of anemia, increased urinary excretion of tryptophan, histidine, phenylalanine and other amino acids.
It is used for 62-hypo- and beriberi, various diseases of the eye membranes (iritis, keratitis, corneal ulcers), radiation sickness, intestinal diseases, a general decrease in feeding, to stimulate hematopoiesis, increase the protective function of the liver, skin.
Prolonged use in excessive doses can lead to nephrolithiasis.
Riboflavin mononucleotvd (riboflavinophosphate, flavin mono-Nucleotide).(7,8-Dimethyl-10-(1-D-ribinyl)-isoalloxazin-5"-sodium phosphate; or riboflavin-5"-sodium monophosphate. Crystalline powder yellow color, odourless, bitter taste, hardly soluble in water. Solutions withstand 30-minute sterilization by boiling, decompose in the light.
Riboflavin mononucleotide - finished form a coenzyme formed in the body from riboflavin (vitamin B2). Like cocarboxylase in biological action, it approaches vitamins and enzymes, being a product of riboflavin phosphorylation.
In combination with a protein, riboflavin mononucleotide is part of the enzymes involved in redox processes. In addition, it plays a role in protein and fat metabolism.
It is used for hypo - and avitaminosis B2, chronic eczema, eye diseases and as a general tonic. Store in a place protected from light.
Flavinat. P-(Riboflavin-5")-P2-(adenosine-5")-diphosphate disodium salt. Yellow-orange crystalline powder, easily soluble in water. It is a coenzyme formed from riboflavin, obtained synthetically.
It acts on the body like riboflavin and is used in the same cases.
Nicotinic acid [vitamin PP (Vz)]. Pyridinecarboxylic-3 acid; close in structure to its amide (nicotinamide). White crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water and alcohol; sterilize the solutions by boiling for 30 minutes.
Contained in meat, fish, kidneys, yeast, grains and products of its processing. In leguminous plants it is in an easily digestible form. The source of nicotinic acid is tryptophan, which can partially replace it.
Dogs, pigs are not able to synthesize nicotinic acid, therefore they constantly need to receive it with feed, while horses, cows, sheep, birds can synthesize it. Nicotinic acid and its amide play an essential role in the vital activity of the body, being prosthetic groups of enzymes codehydrase I (NAD) and codehydrase II (NADP), which carry out redox processes. Nicotinic acid is involved in the processes of glycolysis and proteolysis, increases blood clotting, normalizes hematopoiesis, function thyroid gland, adrenal glands, contributes to the normal functioning of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, affects the rate of growth and development of young animals, has a detoxifying effect, and has a vasodilating effect.
With a lack of nicotinic acid in animals, pellagra develops (in pigs, dogs), disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (enteritis, anacid gastritis), necrotic lesions of the large and caecum are observed, the overall resistance of the body decreases, anemia develops, and symptoms from the side are often expressed. nervous system (paresis, convulsions, muscle tremors, decreased tone of striated muscles). Birds develop inflammation of the tongue, paralysis, they lag behind in growth, plumage is disturbed, dermatitis develops, peeling of the skin on the legs, around the eyes and beak.
In therapeutic doses, nicotinic acid is non-toxic, but in large doses it can be dangerous, because when the acid breaks down in the body, its metabolites capture free methyl groups, resulting in a deficiency of lipotropic factors (choline, etc.) with the development of fatty liver and others. violations.
It is used for pellagra, liver diseases, vascular spasms, long-term non-healing wounds, ulcers, gastrointestinal diseases, heavy metal salt poisoning, radiation sickness, eczema, adrenal insufficiency, coronary circulation disorders, burn shock, sulfonamide poisoning, to stimulate erythropoiesis, growth in suckling piglets and weaners.
Nicotinamide. Amide of nicotinic acid. White fine-crystalline powder, easily soluble in water and alcohol.
Animals tolerate nicotinamide much better than nicotinic acid. It stimulates the secretory-enzymatic function of the gastrointestinal tract, activates the detoxification function of the liver by increasing its glycogen stores, and increases the level of polypeptides and nitrogen in the blood.
The mechanism of action of nicotinamide is similar to nicotinic acid. Nicotinamide, interacting with D-ribose, forms a nucleotide, which is an integral part of the coenzymes of dehydrases - di - and triphosphopyridine nucleotides, which form enzymes of redox reactions in animals.
Nicotinamide is part of the adenylic acid system.
Doses and indications for use are similar to nicotinic acid.
Choline (vitamin B4). Methylated derivative of b-amino-ethyl alcohol. Colorless syrupy hygroscopic liquid alkaline reaction, soluble in water and alcohol. Its hydrochloride salt, choline chloride, is a colorless, highly hygroscopic substance. Used in animal husbandry. Produced with a filler in the form of a dry concentrate.
A lot of choline is found in the liver, meat of cattle, kidneys, cheese, yolks chicken eggs, tomatoes. The largest amount of vitamin in legumes (1.5-3.0 g/kg), fishmeal (3 g/kg). Choline is included in cell structures as an integral part of phospholipids and is a supplier of methyl groups in methylation reactions. Its main functions in the body as a lipotropic factor are also associated with the formation of acetylcholine, methionine and other compounds.
With B4-avitaminosis, all animals are characterized by fatty infiltration of the liver, degenerative changes in this organ and kidneys, anemia, hypercholesterolemia, etc. The most specific symptom is a violation of fat metabolism. With a lack of B4 in the diet of chickens, turkeys, perosis occurs, followed by obesity and cirrhosis of the liver; in adult birds, a decrease in growth and egg production is noted. In piglets - movement disorders, fatty degeneration of the liver, renal necrosis, increased acid-base balance in the blood, reduced viability.
Choline is used to activate methylation processes, treat and prevent fatty infiltration of the liver; as remedy with acute hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver; to improve resorption and absorption of fats; to activate hematopoiesis, accelerate the growth of chickens and piglets.
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). Widely distributed in nature: in yeast, liver, eggs, cereals, cabbage. Synthesized by intestinal microflora. In the body, the dextrorotatory isomer of vitamin B5 is involved in the formation of coenzyme A, which is involved in the oxidation and biosynthesis of fatty acids. Participates in oxidative decarboxylation of keto acids, synthesis citric acid, corticosteroids and acetylcholine.
Insufficiency of pantothenic acid is accompanied by fatigue, dyspeptic disorders.
Apply Calcium pantothenate With neuritis, neuralgia, some allergic reactions, respiratory diseases, ulcers, burns, to eliminate the toxic effects of streptomycin and arsenic compounds.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6, adermin, hexabetaline,Bedokhin). 2-Methyl-3-hydroxy-4,5-di-(hydroxymethyl)-pyridine hydrochloride. White fine-crystalline powder, odorless, bitter-sour taste. Easily soluble in water. Solutions are sterilized by boiling. It is synthesized by plants, yeast cells and symbiotic microflora in the rumen of ruminants. IN pure form isolated from the liver, yeast; obtained synthetically. It is part of coenzymes and participates in the processes of transamination, protein and fat synthesis, and the intermediate exchange of amino acids: tryptophan, methionine, cystine, glutamic, etc.
Reduces capillary permeability, prevents the occurrence of histamine edema, reduces the activity of hyaluronidase.
Used during pregnancy, exhaustion, hypochromic anemia, hyperexcitability nervous system, edematous disease of piglets, skin diseases, liver diseases, as an antiemetic, to improve the regeneration of the epithelium of the eye, the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, with pellagra, radiation sickness, to prevent possible complications when using sulfonamides and antibiotics.
Pyridoxal phosphate. 5 "-Phosphoric ester of 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-formyl-5-hydroxymethylpyridine. Light yellow crystalline powder. Unstable in the light. Slightly soluble in water and insoluble in alcohol. It has the properties of vitamin B6, has a rapid therapeutic effect.
Applied in violation of pyridoxine phosphorylation, skin diseases (urticaria, eczema) and in the same cases as pyridoxine.
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12, anacobin, cycobemin, rubra-Ming, vibicon And etc.). Coa-[a-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl)]-sorcobamide cyanide, or a-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl)-cobamide cyanide. Odorless dark red crystalline powder. Hygroscopic. Difficult to dissolve in water; solutions have
Red or pink color. Sterilize them by boiling for 30 minutes. Oxidizing and reducing substances and salts of heavy metals contribute to the inactivation of the vitamin. characteristic chemical feature cyanocobalamin molecules - the presence of a cobalt atom and a cyano group in it, forming a coordination complex.
In animals, vitamin AT 12 It is synthesized by the intestinal microflora, resorbed and deposited in the kidneys, liver, intestinal wall. Is a growth factor; necessary for normal hematopoiesis and maturation of red blood cells; participates in the synthesis of labile methyl groups, nucleic acids; contributes to the accumulation in erythrocytes of compounds containing sulfhydryl groups; participates in the metabolism of amino acids and carbohydrates; favorably affects the functions of the liver and nervous system. Promotes transformation folic acid into folinium, which is a direct stimulant of hematopoiesis. Stimulates the growth and development of calves (up to 2 months of age, when the physiological inferiority of the scar is observed); improves the acid-base balance of the body; raises the content total protein in blood serum; increases the amount of y-globulins, increases the level of opsonophagocytic reaction in the body of calves, stimulates the production of antibodies.
It is used for anemia, neuritis, paresis, osteoarthritis, liver disease, disorders of the detoxifying function of the liver, radiation sickness, chronic poisoning with salts of heavy metals, organic dyes, dysfunction of the digestive system, pancreas, to stimulate the growth and development of calves, piglets, chickens, increase productivity of laying hens, pregnant animals to improve intrauterine development of the fetus.
Vitamin B12 gives high therapeutic efficacy in combination with antibiotics, nitrofurans in the treatment of diarrheal diseases in suckling pigs and dairy calves.
Mukovit B12- Tablets containing 50 and 500 mcg of vitamin B12 and required amount internal factor. Applied inside for the treatment of B12-hypovitaminosis, alimentary anemia of suckling pigs, increasing the growth rate of chickens.
Oxycobalamin. Dark red crystals or crystalline powder. Hygroscopic. Let's dissolve in water, it is a little - in alcohol.
Metabolite of cyanocobalamin. By pharmacological action, it is close to it, but it quickly turns into an active coenzyme form in the body and lasts longer in the blood, since it binds more strongly to plasma proteins and is more slowly excreted in the urine. Indications for use are the same as for cyanocobalamin.
Cobamamide. Coa-[a-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl)]-Soradeno-zylcobamide. Dark red crystalline powder. When introduced into the body, vitamin B12 is converted into a cobamide coenzyme (cobamamide), which accumulates in the liver tissues. Has a specific activity of vitamin B12 healing effect not only in B12-deficient conditions, but also in diseases of the nervous system, hypotrophic processes, as well as anabolic activity.
Vitogeyut. Obtained from fresh bovine liver. Transparent liquid of yellow or pinkish-yellow color. Preserved with phenol. Contains cyanocobalamin (10 mcg per 1 ml), folic acid and other anti-anemic factors found in the liver. It is used as an antianemic agent for chronic liver damage, atrophic gastritis.
Compolon. A concentrated aqueous extract of the liver of cattle or marine animals. A clear dark yellow liquid containing vitamin B12 and other liver tissue substances. It is used for anemia in piglets and other animals (bovine babesiosis). With hypochromic anemia combined with iron preparations.
Antianemin. An aqueous extract from the liver of cattle with the addition of 1.67 mg of cobalt sulfate.
Indications and doses are similar to Compolon.
Calcium pangamat (vitamin B15, calgam). Calcium salt of ester of gluconic acid and dimethylglycine. White or white powder with a yellowish tint, soluble in water. Hygroscopic. It improves lipid metabolism, increases the uptake of oxygen by tissues and the content of creatine phosphate in the muscles and glycogen in the muscles and liver, eliminates the effects of hypoxia, takes part in the biosynthesis of choline, methionine, adrenaline, steroid hormones.
Pangamic acid is effective for intoxication with hydrocyanic acid, ethanol, tetracyclines, dichloroethane. Under its influence, the production of hormones of the adrenal cortex increases. Vitamin B15 is a donor of methyl groups and is effective in liver diseases (cirrhosis and hepatitis). Vitamin B15 activates the Krebs respiratory enzymes, reduces the content of lactic acid in the muscles.
Used for emphysema, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, to improve the tolerance of sulfanilamide drugs, corticosteroids, itchy dermatoses, myocarditis, poisoning with carbon tetrachloride, salicylates, ethanol.
Folic acid (vitamin Vs, folacid, folicil, niofolin). N- (4 "- [(2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-pteridyl) - methyl] - aminobenzoyl) -X (+) - glutamic acid. Yellow fine crystalline powder, decomposes in the light, hygroscopic, poorly soluble in water. Participates in the process of hematopoiesis, synthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids, purines, pyramidins, in the metabolism of choline, together with vitamin B12 stimulates erythropoiesis, promotes the maturation of erythrocytes. intrauterine development fetus.
The state of folate metabolism also depends on the provision of the body with vitamins C and B12. Folic acid deficiency is observed in gastrointestinal diseases, with a lack of protein in the diet, treatment with sulfonamides. At acute insufficiency folic acid disrupts granulopoiesis; the toxic form of beriberi is accompanied by aleukemia and agranulocytosis. With nutritional folate deficiency in animals, including birds, macrocytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, growth retardation, etc. develop.
Used for various anemias, agranulocytosis, leukopenia different shapes, insufficiency of the detoxifying function of the liver, drug poisoning, radiation damage, with hapochromic anemia, hypofunction of the endocrine glands; the best results are obtained from the combined use of it with vitamin B12 or liver preparations.
Orotic acid (vitamin B13. Crystalline powder, poorly soluble in water. Participates in the synthesis of pyramidal nucleotides in the liver, nucleic acids, bilirubin, phospholipids, increases the content of folic acid in the liver, stimulates the fertility of animals, the intensity of the growth rate of young animals.
With a lack of orotic acid in the body of animals
The growth rate of young animals decreases, bone marrow hematopoiesis, protein and carbohydrate metabolism are disturbed, and the detoxifying function of the liver decreases.
Vitamin B preparations - 2.5 out of 5 based on 2 votes
B vitamins in tablets are an easy way to improve your health. In nature, these substances are found in various types fruits, vegetables, and meats. They are very useful for the body, favorably affecting the nervous system, are involved in improving the functioning of the brain, and also maintain the overall tone of the body in good condition. The lack of these organic substances can lead to various diseases, however, there are cases when an overabundance of one "representative" of this group led to the development of pathologies. It is known for sure that they are necessary for a person in the autumn and spring periods, when they need support.
The benefits of B vitamins
If you take then you can achieve recovery. Now consider the effect of these substances on the body.
- B1 (thiamine) - participates in the digestion process, helping the absorption of fats, proteins and carbohydrates;
- B2 (riboflavin) - improves metabolic processes and enhances the visual abilities of the body. It also affects the condition of the skin and synthesizes hemoglobin;
- B3 (nicotinic acid) - synthesizes proteins and fats, releases energy from nutrients;
- B4 (choline) - improves memory, is involved in the transport of fats in the liver;
- B5 (pantothenic acid) - forms useful cholesterol in the body;
- B6 (pyridoxine) - regulates the activity of the nervous system, regenerates red blood cells, forms antibodies;
- B7 (biotin) - releases energy from compounds that contain calories;
- B8 (inositol) - normalizes sleep, restores nerve tissue, improves skin turgor and helps to reduce the accumulation of fat in the liver;
- B9 (folic acid) - participates in the formation of red blood cells and promotes the formation of nucleic acids;
- B10 (para-aminobenzoic acid) - helps the body absorb protein, participates in the work of the intestines, creates red blood cells;
- B11 (levocarnitine) - improves the ability to exercise for a long time, increases the efficiency of the brain, heart, kidneys and muscles;
- B12 (cyanocobalamin) - supports the development of the nervous system, is involved in the creation of red blood cells.
Unfortunately, not all units from the presented group can be found in preparations. Most often they contain B1, B2, B6, B12.
The difference between synthetic vitamins
Tablets created synthetically differ from naturally formed tablets in that the former have the same cellular structure. Each natural vitamin can be compared with the structure of snowflakes: for each of them it is individual and unique. It also happens with natural vitamins that are produced by the human body or found in food. Synthetic organic compounds do not differ from each other in terms of molecular structure. This does not affect their ability to assimilate in any way. Thus, B vitamins in tablets can compensate for the lack of these substances.
Preparations
There are many medical devices, which contain a synthetic analogue of organic substances. Vitamins of group B in tablets are produced by the pharmaceutical company Unipharm Inc. in the Vitrum line, as well as by Hikma Pharmaceuticals in the form of the drug Neurovitan. This is one of the most popular and effective complexes that can improve the overall tone of the body. Consider the composition of each of the above drugs
- "Vitrum Superstress" is intended for people who have experienced stress and need support. The components of the drug compensate for the vitamin deficiency and thereby improve the functioning of the whole organism. The composition of the drug includes such a B-complex: B1, B2, B6, B12, nicotinamide, folic acid.
- "Neurovitan" also has a positive effect on the nervous system, due to the good vitamin composition: B1, B2, B6, B12.
The B-complex is also found in brewer's yeast, the Alfavit series of bioadditives and the Doppelhertz dietary supplement. It should be noted that the medication should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Thus, B vitamins in tablets are presented in a wide pharmaceutical assortment, and, based on personal preferences and trust in the manufacturer, you can choose one of them.
A small child under 10 years of age needs almost 4 times more B vitamins than an ordinary adult. Vitamins of this group are contained in many foods, as well as in special vitamin complexes that can be purchased at a pharmacy. Overdoing it with volumes will not work, because the excess will simply be excreted from the body, but if there is a shortage, then problems can begin. Children and adults begin to get tired more, anemia appears, mood worsens, and appetite goes to zero. What are the benefits of B vitamins and how to make up for their deficiency?
B vitamins are found in various foods, and their excess is excreted from the body very quickly.Benefits of B vitamins
All vitamins of this group are similar in the following aspects: they provide metabolism, form the skeleton and muscles, are participants in the synthesis of blood, in particular antibodies that can prevent the appearance infectious diseases and cancerous growths. Useful elements have a great effect on the health of the heart, blood vessels and nervous system.
Water-soluble vitamins of this group each have their own properties and their effects on the body. Micronutrients will work with maximum efficiency if they enter the body at the same time. A poor diet with a deficiency of nutrients in most cases is deprived of almost all vitamins of this group. List over time organic compounds Group B was revised and modified several times, today it is a group of 9 main elements:
| Name | Main functions | Deficiency symptoms |
| B1 or thiamine | A participant in metabolism, contributes to the work of the heart and blood vessels, and also ensures the full functioning of the nervous system. | Fatigue, loss of appetite, digestive disorders, heart failure, muscle weakness, anxiety. |
| B2 or riboflavin | A participant in protein and lipid metabolism, contributes to the full development of the baby, ensures the good condition of the mucous membranes and skin. | Skin diseases, nervous diseases, diseases of the mouth and mucous membranes, metabolic disorders, anemia. |
| B3 or nicotinic acid | It has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the circulatory and nervous systems, as well as on the activity of the adrenal glands. | Decreased appetite, stool disorders, muscle weakness, bad dream, irritability, dry skin. |
| B4 or choline | Helps the work of memory and attention, promotes the activity of the nervous system, participates in the metabolism of fats. | Increase in body weight, blood cholesterol levels. Violations of memory, attention. |
| B5 or pantothenic acid | Forms and maintains the level of hormones, ensures the smooth functioning of the nervous system, is responsible for the immune system. | Pain in muscle tissue, pain in the head, drowsiness, poor vision, dry skin. |
| B6 or pyridoxine | Actively participates in hematopoiesis, in protein metabolism. | Dermatitis, diseases of the heart and blood vessels, anemia, conjunctivitis. |
| B7 or biotin | Normalizes the volume of sugar, helps the full development and functioning of the nervous system. | Seborrheic dermatitis in newborns, nervousness, fatigue, low hemoglobin levels, skin inflammation. |
| B9 or folic acid | Member of protein metabolism, assistant in the field of hematopoiesis. | Liver disease, sleep disturbances, anemia, red tongue, bleeding gums, problems with the digestive system. |
| B12 or cobalamin | The main participant in hematopoiesis, an active "actor" in the metabolic process, helps to improve mental activity. | Rapid fatigue, passivity in sensory and motor terms, inflammation in the oral cavity, stomach pain, weight loss, constipation. |
 Fatigue May cause vitamin B1 deficiency
Fatigue May cause vitamin B1 deficiency Daily rate
Consider the existing table:
| Age | Daily requirement, mg | ||||||||
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B9 | B12 | |
| 0-6 months | 0,4 | 0,5 | 15 | 100 to 350, determined by the doctor | 2 | 0,1 | 44105 | 40 | 0,4 |
| 6-12 months | 0,5 | 0,6 | 15 | 3 | 0,3 | 44105 | 60 | 0,5 | |
| 1-3 years | 0,8 | 0,9 | 15 | 42463 | 0,5 | 44105 | 100 | 0,9 | |
| 4-6 years old | 0,9 | 1 | 15 | 42463 | 0,6 | 20-40 | 200 | 1,2 | |
| 7-10 years old | 1,2 | 1,4 | 15 | 42494 | 1 | 20-40 | 200 | 1,2 | |
| Boys, 11-14 years old | 1,4 | 1,7 | 15 | 42555 | 1 | 20-40 | 200 | 1,8 | |
| Boys, 15-18 years old | 1,5 | 1,8 | 15 | 42555 | 1,3 | 50 | 200 | 2,4 | |
| Girls, 11-14 years old | 1,3 | 1,5 | 15 | 42555 | 1 | 20-40 | 200 | 1,8 | |
| Girls, 15-18 years old | 1,3 | 1,5 | 15 | 42555 | 1,2 | 50 | 200 | 2,4 | |
Products
Most of the compounds in this group are found in:
- yeast;
- dairy products - cheese, milk, cottage cheese;
- germinated grains;
- liver;
- legumes;
- green vegetables;
- fish;
- eggs;
- nuts.
As you can see, the most ordinary products can boast and please the content. beneficial trace elements. Their beauty also lies in the fact that even heat treatment is not able to destroy them. A nursing woman should carefully ensure that her diet is varied and balanced. As for the grown-up child, who has already begun to try complementary foods and is approaching a complete transition to adult food, he will need to be replenished. daily diet some of the products listed above.
 Dairy products and eggs contain a large number of b vitamins
Dairy products and eggs contain a large number of b vitamins Complete nutrition it is not always possible or not always possible, therefore it is possible to compensate for the deficiencies of some vitamins using vitamin complexes. When a child has some of the above symptoms, reflecting a lack of useful micronutrients, then you should definitely start to make up for their deficiency, but before that, be sure to consult a doctor.
Multivitamin complexes
B vitamins, acting together, have an effect on the body maximum effect, so doctors usually recommend taking them in the form of complete vitamin complexes. All vitamin preparations are balanced in composition and have minimal risk occurrence of allergic reactions. Nevertheless, it will not be superfluous to monitor the condition and well-being of the child in the first days of admission.
Redness or rash that appeared in the first three days requires the abolition of the selected remedy and the selection, together with the doctor, even more safe option. Vitamins should be stopped if the child has vomiting or diarrhea. Postponing the use for a while, you can continue the treatment course after eliminating all ailments.
In some cases, according to medical indications, intramuscular injections can be prescribed, but even this procedure can be replaced by taking tablets or capsules with microelements of group B. Dr. Komarovsky says the following about this: “Vitamins will be perfectly absorbed with their usual use. The injection option is practiced only if the child does not have the opportunity to swallow the pills on his own.
Vitamins from the Multi-Tabs series
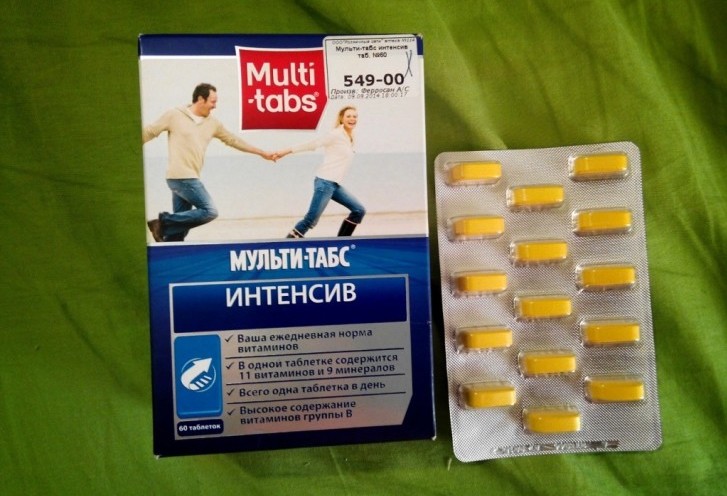 Multi-Tabs Intensive is suitable for adults and children over 12 years old
Multi-Tabs Intensive is suitable for adults and children over 12 years old - - in this complex there are vitamins not only of group B (B12, B6, B1, B2 and others), but also A, C, D, E. In addition, the microelements included in the composition will provide invaluable benefits to the body: calcium, iodine, selenium, iron , copper, magnesium, chromium, zinc. The minimum age for admission is 12 years. Take the drug should be 1 tablet in the morning after meals.
- A drug "Multi-Tabs V-Complex" includes the following substances: riboflavin, pyridoxine (B6), thiamine (B1), pantothenic acid, folic acid and cyanocobalamin (B12). May be used by children over 12 years of age. Take the drug should be 1 tablet 1 to 3 times a day. Reception is preferably carried out during meals or immediately after it. Minimum term therapy - 2 months.
- For kids more younger age exists children's version vitamin complex. It's called "Multi-Tabs Kid". He has the same dosage, only it is recommended to crush the tablet before taking it.
Vitamin preparations "Pikovit"
This series is adapted for children early age. Everything is taken into account here age features child.
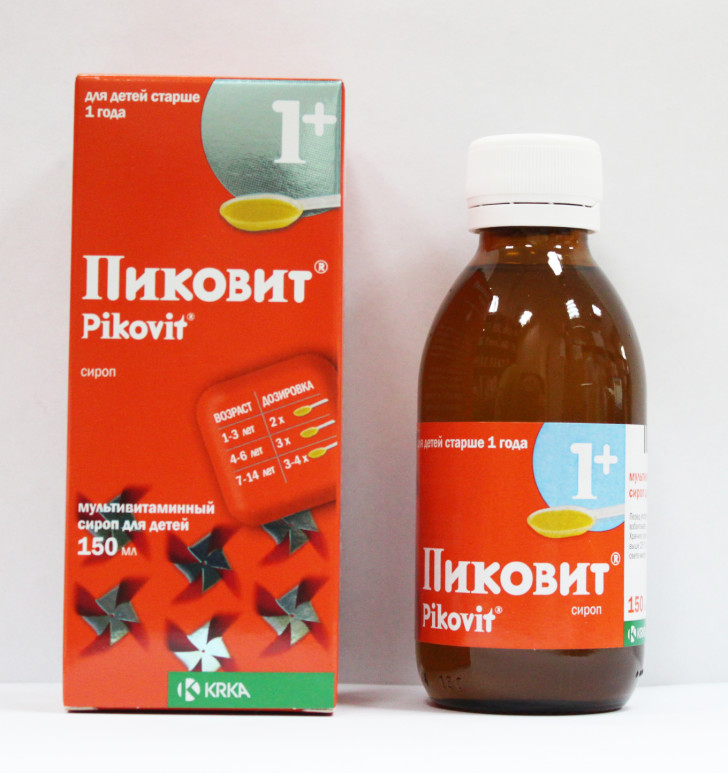 The syrup can be used for children from 1 year old.
The syrup can be used for children from 1 year old. - Means "Pikovit syrup" with a large amount of vitamins (A, D, C, PP, B2, B6, B1, B12, BB) is allowed for use by children from 1 year old.
- In the preparation "Pikovit omega-3" all the vitamins contained in the syrup are present (A, D, C, PP, B2, B6, B1, B12, BB), plus omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E. It can be taken by children over 3 years old.
- "Pikovit complex" is allowed for use by children from the age of three. The composition of this drug is rich in vitamins (B2, B6, B1, B12, BB, A, D, C, PP) and minerals. Available in pharmacies in the form of chewable lozenges.
- Means "Pikovit Plus" has an expanded composition in terms of volume. Elements such as calcium, iodine, zinc and iron are present in higher concentrations. Chewable tablets of this type are recommended for children over 5 years of age.
- In Pikovit Forte multivitamins, all vitamins (A, D, C, PP, B2, B6, B1, B12, BB) and minerals have a double dose. This type of series is intended for schoolchildren (from the age of 7), because it is during this period that children experience a sharp increase in not only mental, but psychological stress. The child gets into a stressful environment, and our task is to help and protect him as much as possible. The complex can be used as prophylactic to exclude autumn and spring beriberi.
 Pikovit vitamins contain a double dose of vitamins and minerals
Pikovit vitamins contain a double dose of vitamins and minerals Application features
As we wrote above, it is better to take B vitamins all together. The only exception is thiamine (B1), which does not combine well with riboflavin and cobalamin (B12). The dosage of all micronutrients must be carefully calculated.
All vitamin elements work well with zinc, iron and calcium, helping to make these minerals easier to absorb. Scientific evidence is available regarding a positive response to these drugs in an organism weakened by emotional stress, as well as in people with distracted attention and difficulties in cognitive processes.
Contraindications and overdose
It is impossible to oversaturate with vitamins, such cases are very rare, because the excess is absolutely easily excreted from the body. Of course, the dose must be strictly observed. Too much of the drug, taken at one time, can lead to intoxication of the body. Following this, there will be disturbances in digestion and in other systems of the human body.
Treatment of diseases
Children's diseases are often treated together with the use of vitamin complexes, which no longer just provide prevention, but also participate in the treatment. The indications are as follows:
- hypovitaminosis of varying degrees;
- severe infectious diseases;
- neurological diseases;
- postoperative period, rehabilitation.
 The intake of B vitamins is prescribed, including for hypovitaminosis
The intake of B vitamins is prescribed, including for hypovitaminosis To kid infancy may be assigned a specific vitamin complex with elements B1, B12, B6 and others, but only after a thorough diagnosis. It is important to know that some drugs, for example, Neuromultivit, are categorically contraindicated for children with existing diseases: bronchial asthma, diseases of the intestines and stomach, allergic manifestations, individual intolerance to one or more components. Babies under the age of 1 year should take these drugs only under the strict supervision of a doctor, if such treatment is required, then the dose is usually calculated as follows: ¼ tablet 2 times a day. The dosage will be individual, calculated based on the needs of the child's body in certain substances.
The most convenient forms of release that suit both children and adults are syrup and drops. They should be taken according to the instructions, but usually this is a single dose in the morning after a meal. Some funds, for example, Unicap, are allowed to be taken by children a few months old. In addition to the vitamins we are considering today (B1, B6, B12 and others), they may include vitamin elements A, C, D, E. These include multivitamins with the names Adivit and Polivit Baby. Experienced doctor, knowing the child and its features, will easily pick up desired option and adjust the required dose.
Vitamins are of great importance for normal life human body. They support the functioning of the immune and nervous systems at an optimal level, the growth and development of the body, and are the most important participants in metabolism. Together vitamins cope with the problems of the body much faster than one by one. Improper nutrition leads to a lack of all vitamins at once. Therefore, specialists with hypovitaminosis most often prescribe vitamin complexes.
B vitamins in dietary supplements
A modern pharmacy chain offers the consumer a wide range of B vitamins in tablets.
Brewer's yeast, thanks to the content of B vitamins, relieves the skin of acne, improves the condition of hair and nails, regulates glucose levels and reduces the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
"Doppelgerz Active Magnesium plus B vitamins" is a dietary supplement containing B vitamins and magnesium. Their interaction perfectly affects the work of all organs and systems. Vitamin B together with magnesium normalizes metabolic processes, improves heart function and blood circulation, dilates blood vessels, has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system, has an anti-stress effect, and stabilizes glucose levels. The bioadditive has a number of contraindications: pregnancy and lactation, individual intolerance to the components.
"Alfavit" - dietary supplement with B vitamins in tablets. The use of B vitamins in tablets has a therapeutic effect much faster than the use of a number of products. Even a saturated diet does not always satisfy the body's needs for vitamins and microelements, which can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system and brain. Vitamins that come with food do not have time to accumulate and are quickly excreted from the body. To maintain their optimal amount and ratio in the body, B vitamins are used in tablets, which provide a person with excellent health.
Vitamins of group B in the composition of drugs
Currently, the most popular are some drugs containing B vitamins.
"Neurobion" is a drug intended for the complex treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia and neuritis, stress conditions and mild forms of depression.
Neurovitan has a positive effect on the nervous system. "Vitrum Superstress" is indicated to eliminate the effects of stress. "B-50" is prescribed for diseases of the digestive system - cholecystitis, gastritis, cholelithiasis and dysbiosis; organs of vision - "dry eye" syndrome and reduced visual acuity; stress, neurosis and depression; diseases of the skin, hair and nails.
Neuromultivit and Neurodiclovit are vitamin pills that increase the strength and endurance of the body.
B vitamins are natural substances that enter the human body with food. They are extremely important for normal life. These vitamins play a special role in the activity of the nervous system. If they do not get enough into the human body, then this in itself can lead to malfunctions in the nervous system (in particular, to the occurrence of polyneuropathies). In addition, in a number of pathological processes in the nervous tissue, B vitamins have a therapeutic effect due to their ability to influence metabolism and restore nerve fibers. That is why this group medicines widely used in the treatment of neurological diseases. In recent decades, B vitamins have been used for problems with any parts of the nervous system, because the role of their deficiency has been proven even in the development of thought disorders. This article will focus on the main aspects of the use of B vitamins in neurological practice. You will receive information about the varieties of B vitamins available on the pharmaceutical market and the features of their use.
When talking about the effect of B vitamins on the nervous system, they usually mean the three most important of them: vitamin B 1 (thiamine), vitamin B 6 (pyridoxine) and vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin). It is these substances that are indispensable for the functioning of our brain and nerves.
How do individual vitamins work?
 In order to prevent, it is enough just to eat well, getting the required amount of each of the B vitamins with food.
In order to prevent, it is enough just to eat well, getting the required amount of each of the B vitamins with food. B vitamins are unequal in their effects. Each of them has its own tasks, which we will now talk about.
In 1, it performs the following main roles:
- ensures the processing of carbohydrates by nerve cells, maintaining the energy potential;
- carries out the conduction of a nerve impulse along the peripheral processes of nerve cells (axons), thus realizing the transmission of an impulse;
- is engaged in the construction of nerve cell membranes;
- participates in the healing of damaged nerve processes (regeneration).
In 6 it works like this:
- participates in the synthesis and destruction of biologically active substances that are information transmitters in the nervous system (dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, serotonin and others);
- regulates protein synthesis and fat metabolism;
- ensures the transmission of impulses at the point of contact of two nerve cells (synapse);
- fights free radicals, that is, it is an antioxidant.
At 12 needed for:
- construction of the myelin sheath of nerves;
- synthesis of acetylcholine (a substance with which the impulse is transmitted between neurons);
- decrease pain associated with damage to nerve fibers.
Of course, these are far from all the functions of B vitamins. The above is only a small part of their work, relating specifically to the nervous system. And the role for the whole organism is much wider.
In connection with such a key role of B vitamins in metabolic processes in the nervous system, they are usually called neurotropic.
Neurotropic vitamins of this group have unique property: when applied simultaneously, their effect is much higher than just the sum of their individual influences. This means that the simultaneous administration of all three drugs at once is much more effective than their use alone. Therefore, several decades ago, pharmaceutical companies focused their efforts on the creation of combined forms of B vitamins in order to improve the quality of treatment and increase the convenience of using drugs. So, for example, previously it was necessary to perform three different injections so that the patient could receive all three neurotropic vitamins. And today there are drugs that contain all three components in one ampoule. Agree that it is much more convenient and causes less inconvenience to the patient. The same can be said about tablet forms. Complexes of B vitamins in the form of tablets and dragees are available in pharmacies.
Diseases of the nervous system, in the treatment of which vitamins of group B are used
The role of B vitamins in relation to the nervous system is considered to be not fully understood. More and more new information comes after various studies. And in connection with new data, the list of neurological diseases in which neurotropic vitamins have a therapeutic effect is constantly expanding. There are great prospects for them in the future. The list of neurological problems for which B vitamins can be used consists of:
- various kinds of polyneuropathies (first of all, and);
- neuropathies of individual nerves (traumatic, infectious and others);
- neurological complications of osteochondrosis of various parts of the spine (, lumboischialgia, cervicalgia, cervicobrachialgia, thoracalgia, radicular syndromes);
- tunnel syndromes (, tarsal canal and others);
- neuropathic pain (for example, with);
- myelopathy;
- acquired mental disorders, in particular - some varieties;
- pyridoxine-associated epilepsy in children.
The therapeutic effect is to stimulate the healing of nerve fibers and their sheaths, improve nerve conduction. Due to this, the severity of motor and sensory disorders decreases in patients. In addition, with damage to the nervous system, the appointment of vitamins of this group allows you to achieve a distinct analgesic effect in neuropathic pain. Lately The effect of B vitamins on vascular and neurodegenerative diseases is being actively studied. It has already been proven that due to a multi-stage biochemical process, B vitamins can slow down the progression of atherosclerosis and reduce the risk of thrombosis. Therefore, their use can be useful as a prevention of the occurrence of vascular catastrophes of the brain ().
I would also like to dwell on the point that many of the above diseases of the nervous system can sometimes be associated with an insufficient content of the trio of B vitamins in the body. However, there are no other reasons for the occurrence of these diseases. For example, polyneuropathy can occur on its own only with a deficiency of vitamin B 1 or B 6, and a long-term lack of vitamin B 12 can cause damage to the spinal cord. Studies have found that a lack of B vitamins often occurs when:
- irrational nutrition (since the bulk of the vitamins the human body receives from food);
- alcohol abuse (because usually nutrition also becomes inadequate, and the body needs a lot of vitamin B 1 to break down alcohol);
- drug addiction (due to an antisocial lifestyle);
- violation of absorption processes in the intestine (malabsorption syndrome, duodenal ulcer and other diseases);
- after surgical operations on the gastrointestinal tract;
- when taking certain drugs (for example, isoniazid for tuberculosis or diuretics for edema).
It is noteworthy that B vitamins realize their therapeutic effect not only in conditions of their deficiency. Due to the peculiarities of participation in the metabolism, their rather large doses are necessary for the body to fight many diseases and in cases where there is no shortage of them.
Features of the use of B vitamins
 In the pharmacy network, you can buy each of the B vitamins individually or a mixture of them in one ampoule
In the pharmacy network, you can buy each of the B vitamins individually or a mixture of them in one ampoule B vitamins are water-soluble, which allows them to be easily absorbed when taken orally and interact with the body's natural environments. However, vitamin B 1 in small doses in the form of tablets is destroyed in the intestines by enzymes, respectively, it is poorly absorbed. If you try to increase the dose, then this generally leads to a blockade of the transfer of the vitamin from the intestines to the blood. How to be? Medicine has found a way out of the situation. Sufficient concentrations can be achieved by parenteral administration, as well as using a fat-soluble form of vitamin B 1 that is able to dissolve in fats. This form of vitamin B1 is called Benfotiamine. Benfotiamine is resistant to the effects of gastrointestinal enzymes, which makes it possible to achieve the absorption of large doses and achieve the required concentration of the drug in the blood.
Another feature of the application is the following: individual vitamins B 1 , B 6 , B 12 cannot be used as a joint injection with one syringe, that is, as a mixture. The fact is that in a pharmacy these vitamins can be purchased separately (vitamin B 1 ampoules, vitamin B 6 ampoules, vitamin B 12 ampoules). In these cases, it is strictly forbidden to combine a solution from one ampoule with a solution from another in one syringe. But given the frequent need simultaneous use these vitamins, the pharmaceutical industry has solved this problem. Mixtures of these vitamins were synthesized, which are already mixed in one ampoule and do not inactivate each other, but rather enhance the effect. Since then, if it is necessary to use all three vitamins at the same time, only such mixtures made by an industrial method are prescribed. Some of them also contain Lidocaine, which is an anesthetic. It is able to enhance the analgesic effect of B vitamins, as well as make the injection itself insensitive to the patient.
The next feature of the use of B vitamins is a potentially allergic reaction to them. In principle, any medicinal substance may not be individually tolerated by patients; it is impossible to predict such a reaction. But you should be more careful with vitamins B 1 and B 12. Allergy to these vitamins, although rare, still happens, so this fact must be taken into account by both medical personnel and the patient.
List of B vitamins that can be found at the pharmacy
The world of business also affects the pharmaceutical industry. Regarding the B vitamins, it looks like this: the main three vitamins are represented by a huge number of drugs. That is, a variety of drugs have the same active composition. The difference lies only in the manufacturer and sometimes in additional substances, and, of course, in price. Some manufacturers claim that the degree of purification affects the effectiveness of the drug. We do not undertake to evaluate B vitamins by this indicator. Let's compare them only in composition and forms of release. In order not to get into a mess and not overpay for the same substances, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the list of B vitamins below.
So, the most common complexes of B vitamins are:
- Milgamma;
- Combilipen;
- Vitakson;
- Vitagamma;
- Binavit;
- Neurorubin;
- Neurobion;
- Compligam B;
- Trigamma.
What do all these drugs have in common? All listed drugs are available in the form of solutions for intramuscular injections. 1 ampoule of any of them contains 100 mg B 1, 100 mg B 6 and 1 mg B 12. As you can see, the active ingredients are absolutely identical both in composition and in dosages. Some of the drugs in their composition additionally contain 20 mg of Lidocaine for an analgesic effect (all of the above, except Neurobion and Neurorubin). There is one more difference: Neurobion and Neurorubin in one ampoule contain 3 ml of solution, and all the rest - 2 ml each. However, this does not affect the total dose. That is, to get the same amount of mg of vitamins, you need to inject, for example, Combilipen 2 ml, and Neurorubin 3 ml.
And, of course, the price. According to this indicator, all drugs differ significantly from each other. Produced abroad are much more expensive than domestic counterparts. However, their similarity in composition and dosages allows you to choose a medicine that everyone can afford.
In addition to the form of release in the form of a solution for injection, all of the above drugs, except for Trigamma, Vitagamma and Binavit, are also available in the form of tablet forms or dragees for oral administration. This provides a continuous course of treatment for certain conditions in neurology, which is very convenient. The composition and dosage in the case of tablet forms is much more diverse than injection forms. Let's dwell on this moment in more detail.
Milgamma compositum (this is what the dragee is called) and Vitakson contain a fat-soluble form of vitamin B 1 (benfotiamine) 100 mg and vitamin B 6 100 mg. Combilipen tabs contains the same amount of benfotiamine and vitamin B 6 as Milgamma, but in addition also 2 μg of vitamin B 12. Neurobion consists of 100 mg of thiamine, 200 mg of pyridoxine and 200 mcg of cyanocobalamin (the manufacturer writes that each tablet contains an excess of vitamin B 12 in the form of an additional 20%, that is, only 240 mcg is obtained). Neurorubin - Forte Lactab contains 200 mg of vitamin B 1 (not benfotiamine!), 50 mg of vitamin B 6 and 1 mg of vitamin B 12. Compligam B complex contains a whole set of B vitamins:
- 5 mg thiamine (vitamin B 1),
- 6 mg pyridoxine (vitamin B 6),
- 6 mg riboflavin (vitamin B 2),
- 0.6 mg folic acid (vitamin B 9),
- 9 mcg cyanocobalamin (vitamin B 12),
- 60 mg nicotinamide (vitamin B 3),
- 15 mg pantothenic acid (vitamin B 5),
- 150 mcg of biotin (vitamin B 7),
- 100 mg choline (vitamin B 4),
- 250 mg of inositol (vitamin B 8),
- 100 mg para-aminobenzoic acid (vitamin B 10).
As you can see, tablet forms are very different in doses and composition, which means that they can not always serve as an identical replacement for each other.
There are B vitamins, which so far have only tablet forms. Neuromultivit, Neurobeks and Neurovitan are widely distributed among them. Neuromultivit is similar to Neurobion in composition. Neurobex exists in two forms: Neo (vitamin B 1 50 mg, vitamin B 2 25 mg, vitamin B 6 10 mg, vitamin B 5 25 mg, vitamin B 9 0.5 mg, vitamin B 12 5 mcg, vitamin B 3 100 mg, vitamin C 175 mg) and Forte (vitamin B 1 100 mg, vitamin B 6 200 mg, vitamin B 12 300 mcg). Neurovitan has an interesting composition: octothiamine 25 mg (this is thiamine + thioctic acid, which is an antioxidant), riboflavin 2.5 mg, pyridoxine 40 mg and cyanocobalamin 0.25 mg. It is possible that in the near future, manufacturers of only tablet forms will also produce injectable ones, since often the treatment process first requires the parenteral use of vitamins.
I would like to note the fact that the B vitamins in the composition of these drugs are medicines. They cannot be taken independently and uncontrollably, carelessly thinking that these are just vitamins. Yes, these are vitamins, but in therapeutic dosages, so only a doctor should prescribe them.
From all of the above, it turns out that the arsenal of B vitamins to combat the pathology of the nervous system is very wide. Currently, the attending physician has a choice medicinal product according to dosages and price category which is a definite plus. And given the emerging new information about the role of B vitamins in the functioning of the nervous system, it can be assumed that soon the list of these drugs will be replenished with new drugs with different dosages and composition.
