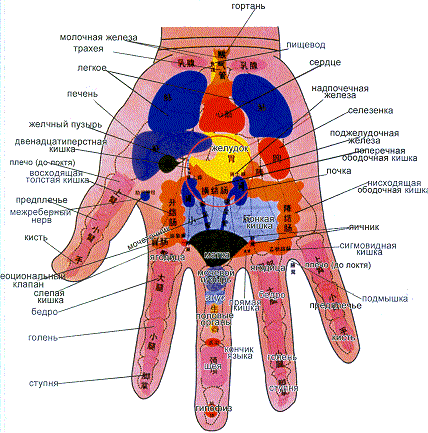
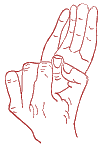
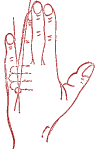
The hands also have points and reflex zones similar to those of the foot.
If you have been to Azerbaijan and some other southern republics, you have probably seen experienced aksakals sorting out the rosary. In the East, it is believed that such rubbing of the fingertips greatly strengthens and calms the nervous system. And the ancient Greek philosopher Anaxagoras even said: “The hand of every person ... is fraught with miraculous power curing diseases." Research by physiologists has confirmed these empirical observations. The nerve endings of the fingers and the entire palm are widely connected with the cerebral cortex. It is no coincidence that the projection of the hand in the cerebral cortex occupies the largest area. Therefore, there are many points and zones on the hand that have a general calming and tonic effect on the body.
So, from the tips to the base of the fingers there is a zone (1), which has the greatest connection with the brain. Therefore, when tired, it is sometimes advised to press with an average force of 3-4 s alternately on the front, back and side surfaces of each finger. Of particular importance is the palmar surface of the middle finger. Here is the zone of the endocrine glands (2). Her stimulating massage is recommended for weakness due to decreased function. thyroid gland. On the back of the hand is the point of life he-gu already known to you (3). Between the folds of the wrist joint is a soothing reflex zone(4) whose massage gives good effect with insomnia, fear, overexcitation. On the ulnar side, between the wrist folds, there is a zone of hysteria (5). Her brake massage will help with hysteria and other neurotic reactions, memory loss, sleep disturbance.
The next zone is called the “examination neurosis zone” (6). It is in the lower third inner surface forearm three transverse fingers above the wrist crease. Her soothing massage relieves pre-exam stress nervous system, prelaunch excitement and others emotional experiences. Zones of points 7 and 8 have been described earlier. Their massage is recommended for general weakness, neurasthenia and other similar conditions. At the inner surface of the elbow crease in the upper third of the forearm there is a zone of cheerfulness, or mental toning (9). It is usually massaged with a stimulating method for lethargy, mild depression.
Due to extensive connections with the cerebral cortex, local fatigue of the muscles of the hands causes inhibition of the central nervous system and a drop in overall performance. Proper conduct acupressure provides good blood flow in the muscles of the hands and emotional stability. Perhaps this allowed the German philosopher I. Kant to say that "... the hand is the brain that has come out."
I hope that the reader now understands how important it is to prevent overwork of the muscles of the hands. Meanwhile, this often happens with people of mental labor who hold a fountain pen for a long time, type on a typewriter, and also during certain types of work that require monotonous coordinated hand movements (assembly of parts on a conveyor, etc.). Quite often even the convulsive reduction of fingers develops. To combat this, swipe acupressure dorsal surface of the hand between the metacarpal bones. Massage in turn each gap between the fingers for 3 minutes using the brake method. Then squeeze the muscles of the hand with force, as in a handshake, and hold in this state for 1 minute. Massage of points 1, 3, 5, 7 helps to more completely relax the muscles.
To relax tired arm muscles
Point 34 (show-san-li, GI10) is symmetrical, located on two diameters thumbs below skin fold elbow bend.Point 35 (qu-chi, Gin) is symmetrical, located in the middle of the distance between the outer epicondyle of the humerus and the outer edge of the ulnar groove.
Point 36 (Lao Gong, MS8) is symmetrical. To find it, squeeze the brush into a fist - the tip ring finger will point to that point. It is located in the middle of the palm. In addition, massage points 1 (he-gu) and 20 (gao-huang).
How to practically choose the most important points? It depends on the nature of the work. For example, for people who often experience hand overload at work (typists, telegraph operators, etc.), it is enough to do self-massage of four points during breaks: 1, 5, 34 and 35. In this case, in the morning before work and during short pauses, an exciting method is used massage. The braking method is applied during the lunch break to allow tired muscles to relax and rejuvenate.
Strengthen your shoulders
If you work in a tense position for a long time, then pain and spasm of the muscles of the shoulder girdle appear. You can even feel that they have become rigid, tough. If you do not pay attention to this, then stiffness of the shoulder joint may develop. Start doing immediately active movements: raising and lowering the shoulder, turning the shoulder forward and backward. Repeat several times. Now massage active points related to the muscles of the shoulder girdle.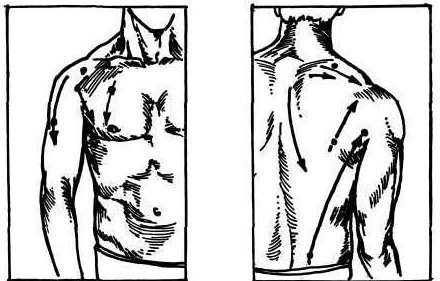
If there is tension and rigidity in the muscles of the outer side, then use the points on the back and shoulders. If you need to relax the pectoral muscles and the muscles that adduct the shoulder, then massage the chest and shoulder along the lines indicated by the arrows in the figure.
Since all these points render mainly local action and are of lesser importance, I will not describe their exact location. It is enough to know the approximate location in accordance with the drawings. If you don’t feel pain with deep pressure, you probably didn’t hit the mark. Therefore, you need to move your finger and put pressure on the nearby area. When the point is found, massage it with a brake method to relax tense muscles. Eliminate these areas of fatigue after any work in a tense posture. It is advisable to supplement this with self-massage of the trapezius muscle, deltoid muscle and shoulder joint.
What are the neck points
To quickly create a working mood, be cheerful all day, develop the will to win, help complete important work, you can do acupressure shiatsu. To do this, place your index fingers on the sides of the neck and press hard 3-4 times on each point on both sides. Then place four fingers on the back of the neck so that the little finger is on the border of hair growth. Press simultaneously with both hands 3 times, then to the right, then to the left. Since nerves and vessels pass close to the surface of the skin on the neck, the pressure on the point should not be more than 3 s.Enhances the effect of massage of the interscapular points. The pressure here is also carried out by the tonic method. Better if someone else does it.
With tedious work at a table with a tilted head, the neck often begins to hurt, often even muscle tension and stiffness of the cervical vertebrae develop. It becomes difficult to turn your head and do any neck exercises. Effective method self-help in these cases is recommended by the Vietnamese doctor Chan-Kuang-Bao.
1. On the tired side of the neck, find those muscles that have become harder than usual due to spasm. Squeeze them firmly with your fingers or the whole palm. In this case, an increase in pain is felt, but you need to be patient a little. Then, with your thumb and forefinger, massage the spasmodic muscle and find the most painful point. Massage it with deep pressure with two fingers for 5 minutes until warm. At the same time, move your neck forward, backward, sideways.
2. Massage point 6 (Xuanzhong, VB39) on the side corresponding to the tired half of the neck. This point affects the tone of the muscles of the neck. Finding the point has been described previously. Feel with your finger in the area of \u200b\u200bthe point a thin cord that goes obliquely to the bone. Squeeze it firmly with your thumb and forefinger. Rub for 5 minutes until a sharp pain appears. Neck movements will become easier. Start them during the massage. If neck movements still remain painful, do a regular massage. First, stroke the palms of your hands from top to bottom.
Then rub with your fingertips the most tired areas of the back of the head, mastoid muscles, the back of the neck (nuchal lines). The force of pressure should decrease from the head to the neck. Then proceed to knead it with the first three fingers. The same fingers are involved in shaking. The massage is supplemented by pressure with the pads of the index fingers on the points of the front side and back of the neck. This relieves tension in the muscles of the cervical-occipital region, improves cerebral blood flow. The latter is also very important.
Do you know the dangers of neck fatigue? It is very difficult to answer this question. It turns out that there is another hidden meaning in the well-known expression "where the neck goes - there the head goes."
It has long been known that with the so-called vegetative-vascular dystonia, as a rule, with a decrease blood pressure Fatigue is the leading complaint in 90% of people. Or maybe you always feel cold, feel lethargic, constantly complain about low blood pressure? Previously, this was explained by poor heredity, malnutrition and other factors. Only about 15 years ago it was found that in many cases such severe fatigue is associated with the development of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine. The most amazing thing is that in some people, its symptoms were detected as early as the age of 15!
They could perform physical activity on average 2.5 times less than their healthy peers. This is due to the fact that with the development of "thorns" and hence muscle seals in the occipital and cervical-collar region, compression and circulatory disturbance in the vertebral artery occur. It also supplies blood to such important parts of the brain as the hypothalamus and the reticular formation. Hence the violation of their functions with the development of vegetative dystonia and unmotivated fatigue already in childhood.
Is it possible to fight this? Undoubtedly. I won't talk about therapeutic measures which will be prescribed by the doctor individually. Your task is to stop the growth of the process, and maybe reverse it with a non-drug method.
I have already mentioned the importance of acupressure for improving cerebral blood flow. But this is only the first step to health. The second will be the fight against seals in the muscles of the neck. Here again will help you point self-massage. Feel for a painful area with hardened skin on your neck. Apply warming creams or ointments around it (Finalgon, St. John's wort, etc.) and rub the skin with a toothbrush for 1.5 minutes. Feeling the warmth in the muscles, press with force on the point with a pad thumb. At the same time, make rotational movements in a spiral. At first, the pain will be very strong. Take a break and continue massaging the point for 10-15 minutes. This should be done carefully, carefully bypassing the places where the pulsation of the carotid arteries is felt. Consistently massage all hardened areas in the neck-collar and occipital areas. Do you feel your neck "burning"?
Repeat this massage for 5 times for each point daily, but without ointment. It is useful at the end of the procedure to put copper discs or plates on the points, which you will learn about a little later. They are reinforced with adhesive tape and periodically pressed during the day. After two or three weeks, you will undoubtedly feel an improvement in well-being and normalization of blood pressure.
I.P. Pavlov wrote: "The activity of the nervous system is directed, on the one hand, to the unification, integration of the work of all parts of the body, on the other hand, to the connection of the body with the environment, to balancing the body system with external conditions" (I.P. Pavlov , 1922).
Structural - functional unit of the nervous system is a neuron (nerve cell). It consists of a body, a process - a dendrite, through which a nerve impulse comes to the body, and a process - an axon, through which the nerve impulse is sent to another nerve cell or working organ. According to the morphological and functional characteristics, three main types of neurons are distinguished:
1) Sensory neurons(extero-, intero- and proprioceptors).
2) Interneuron. This neuron transfers excitation from a sensitive (afferent) neuron to an efferent one.
3) Effector (motor) neuron. The axons of these cells continue in the form of nerve fibers to the working organs (to skeletal and smooth muscles, glands, etc.).
The unified nervous system is conditionally subdivided according to the topographic feature into central and peripheral, according to the anatomical and functional - into somatic and vegetative.
central nervous system
It includes the spinal cord and brain, which consist of gray and white matter. Gray matter is an accumulation of nerve cells along with the nearest branches of their processes. White matter is nerve fibers, processes of nerve cells. Nerve fibers form the pathways of the spinal cord and brain and connect various parts of the central nervous system, nerve centers with each other.
peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of roots, spinal and cranial nerves, their branches, plexuses and nodes that lie in various parts of the human body.
somatic nervous system
The somatic nervous system provides innervation mainly to the body - the soma, namely the skin, skeletal muscles. This part of the nervous system performs the function of connecting the body with external environment with the help of skin sensitivity and sense organs.
autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system innervates all the viscera, glands, involuntary muscles of organs, skin, blood vessels, heart, regulates metabolic processes in all organs and tissues. The autonomic nervous system is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. In each of these parts, as in the somatic nervous system, the central and peripheral sections are distinguished.
Massage manipulations, acting on receptors located in the skin, muscles, joints, ligaments, organs and other tissues, irritate them. This irritation is transformed into a nerve impulse, which is sent through nerve fibers, plexuses, a system of neurons to the working organ, causing functional changes in skeletal and smooth muscles, digestion, blood circulation, lymph flow, in immune, metabolic and other processes. At the same time, massage techniques, unskilled procedures, without taking into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the body, its functional state can cause deterioration general condition person, the appearance of local pain, discomfort and other undesirable side effects.
Drawing a conclusion from the above, we can say with confidence that with the help of massage, you can purposefully change the functional state of the body. There are five main types of massage effects on the functional state of the body: tonic, soothing, trophic, energy-tropic, normalizing functions.
The tonic effect of massage is expressed in the enhancement of excitation processes in the central nervous system. It is explained, on the one hand, by an increase in the flow of nerve impulses from the proprioreceptors of the massaged muscles to the cerebral cortex, and on the other hand, by an increase in the functional activity of the reticular formation of the brain. The tonic effect of massage is used to eliminate negative phenomena in hypokinesia caused by a forced sedentary lifestyle or various pathologies (injuries, mental disorders and so on.). Among the massage techniques that have a good tonic effect, the following can be distinguished: vigorous deep kneading, squeezing, and all percussive techniques (chopping, tapping, patting). In order for the tonic effect to be maximum, the massage must be carried out at a fast pace for a short period of time.
The calming effect of massage is manifested in the inhibition of the activity of the central nervous system, caused by moderate, rhythmic and prolonged irritation of the extero- and proprioreceptors. The calming effect is most quickly achieved by such massage techniques as rhythmic stroking of the entire surface of the body, shaking, shaking, felting, vibration. They must be carried out at a slow pace for a fairly long period of time. It should be noted. Massage techniques such as “kneading” and “rubbing”, depending on the nature of their implementation (tempo, strength, duration), can have a tonic or calming effect on the nervous system.
The trophic effect of massage, associated with the acceleration of blood and lymph flow, is expressed in improving the delivery of oxygen and other tissues to cells. nutrients. Especially great is the role of the trophic effects of massage in restoring muscle performance.
The energotropic effect of massage is aimed, first of all, at increasing the efficiency of the neuromuscular apparatus. Specifically, this is expressed as follows:
- in the activation of muscle bioenergetics;
- in improving the metabolism in the muscles;
- in increasing the formation of acetylcholine, which leads to an acceleration of the transmission of nervous excitation to muscle fibers;
- in increasing the formation of histamine, which dilates muscle vessels;
- in an increase in the temperature of the massaged tissues, leading to an acceleration of enzymatic processes and an increase in the speed of muscle contraction.
Normalization of body functions under the influence of massage
The normalization of body functions under the influence of massage is manifested, first of all, in the regulation of the dynamics of nervous processes in the cerebral cortex. This action of massage is especially important with a sharp predominance of excitation or inhibition processes in the nervous system. In the process of massage, a focus of excitation is created in the zone of the motor analyzer, which, according to the law of negative induction, is able to suppress the focus of congestive, pathological excitation in the cerebral cortex. The normalizing role of massage has great importance in the treatment of injuries, as it contributes to the speedy restoration of tissues and the elimination of atrophy. When normalizing the functions of various organs, as a rule, segmental massage of certain reflexogenic zones is used.
I want to recall one episode from the film "Shield and Sword". Soviet intelligence agent Weiss comes to the next meeting with the underground doctor. “You look bad, Weiss,” the doctor says. “It looks like your nerves are failing. You need to take multiple sessions massage…»
Nervous system and massage? It would seem that there could be something in common between them. Nevertheless, there is a lot in common, because the nervous system is the main regulator of the vital activity of the whole organism. It controls such processes as muscle contraction, metabolism, the work of the heart and endocrine glands. In other words, all processes are carried out under the influence of the nervous system. What about massage? Mechanical stimulus - and only? No, it turns out that it can thoroughly interfere with the activity of the nervous system, helping to direct the processes occurring in the body.
Your child is upset about something. How to calm him down? you start talking sweet words and at the same time stroke the baby on the head, back, arms. It's nothing but soothing massage. Through the nerve endings, it acts on the central nervous system and calms it.
Once, at the World Championships, one of our wrestlers lost a fight. I got upset, drooped, the desire to continue the competition disappeared. The masseur invited him for a massage to restore strength. The athlete left the room cheerful, collected, feeling sports anger. And despite the fact that the opponent was strong and possessed rich technique, our athlete won the match. Naturally, an experienced masseur managed to energize him, mentally set him up and prepare him for a sharp and intense struggle.
Various tricks self-massage act differently on the nervous system. Some soothe (stroking, shaking, rubbing), others excite (squeezing, kneading, tapping, chopping, patting).
Boxer getting ready for a fight. The gong will now sound. The second removes the bench and pats the athlete on the shoulder: “Let's go ... Be bolder!” This is also a kind of massage element.
The effect of massage on the nervous system also depends on how energetically and for a long time the techniques are performed. Massage can also regulate the sensitivity of the skin to painful irritations, soothe pain, and through the skin affect other organs.
How can one not remember such a case? One attentive hairdresser drew attention to the fact that after applying the cream on the face of his clients, patients with hypertension, their blood pressure decreases and their head stops hurting. It turned out that this is not the result of the action of the cream, but massage, which he did by rubbing the cream. Now massage is widely used to treat high blood pressure.
Massage is effective for nervous fatigue, after hard physical or mental work. In this case, it causes pleasant excitement, a feeling of cheerfulness, lightness, and increases efficiency.
However, the role of massage in relieving nervous fatigue for a long time underestimated. I remember that about twenty years ago I had to give a lecture "The role of massage in the system of sports training of high-class athletes" in front of an audience of athletes representing the most different kinds sports. They listened to me with great attention, as everyone understood that with modern psychophysical stress, recovery is indispensable, and massage is the main factor in recovery and treatment. But as soon as I started talking about the peculiarities of massage for chess players, smiles appeared in the hall, remarks were heard: they say, how else do they need massage, chess players?! V. Sazlov supported me, who got up and said that chess is a false sport that requires not only physical strength (for example, when analyzing some games, you have to sit still for five to seven hours), but also a huge mental endurance. So, for example, the world championship match in 1978 in the city of Baguio lasted three months. At the same time, the future winner Anatoly Karpov was massaged daily, and in some cases twice a day.
Match duels of chess players are characterized by long-term competitive activity in a state of extreme mental tension - stress, associated with discoordination of psychophysiological functions. The blood supply to the brain, sleep, appetite are disturbed, working capacity drops sharply, weight “burns”. And in this case massage extremely necessary. Now no one even thinks about whether massage is necessary for chess players. And the chess players themselves became close friends with him.
An experienced massage specialist candidate is currently working with Soviet grandmasters. pedagogical sciences V. Krylov.
Acupuncture points are selected individually for each, depending on the functional state of the muscles and on the tasks set. In sports practice, acupressure is mainly used to relax the tone of spastic muscles and stimulate atonic and hypotonic antagonists. The masseur controls the effect of changing the tone of the neuromuscular system with the hand holding the limb in the distal section. During one massage session, no more than 12 such points should be applied, which significantly affect the state of the musculoskeletal system of the person being massaged. Acupressure can be combined with active or passive movements.
Pressure points for relaxing or stimulating the neck muscles:
FU-TU (Fig. 78) - in the neck area from the side in the center of the abdomen of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level of the line of the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage, drawn parallel to the clavicle.
TIAN-DING - at the posterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level of the line of the lower edge of the thyroid cartilage, drawn parallel to the clavicle.
Rice. 78. The main points of influence on the front surface of the body and their effect on the muscles according to the numbering. 1 - large chest; 2- small chest; 3 - double-headed shoulder; 4 - sternocleidomastoid; 5 - subcutaneous neck.
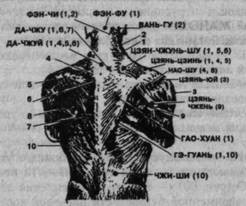
Rice. 79. The main points of influence on the back of the body and their effect on the muscles according to the numbering. 1 - trapezoidal; 2 - sternocleidomastoid; 3- deltoid; 4- supraspinous; 5- muscle that lifts the scapula; 6 - diamond-shaped; 7- deep backs; 8- infraspinatus; 9 - large round; 10 - widest.
WAN-GU - at the posterior edge of the mastoid process at the level of FENG-CHI.
FENG-FU - on the midline between the occipital bone and the 1st cervical vertebra at the level of FENG-CHI.
Influence points for relaxation and stimulation of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and upper limbs:
JI-QUAN (see Fig. 78) - in the anterior part of the armpit at the level of the top of the axillary fold between the pectoralis major and biceps muscles of the shoulder.
ZHOU-ZHUN - in the second intercostal space in the area of the location of the large chest muscle.
DA-ZHUY (see Fig. 79) - in the middle of the distance between the spinous processes of the VII cervical and I thoracic vertebrae.
JIAN-YU - in the area of the shoulder joint between the head of the humerus and the acromial process of the scapula.
FENG-CHI (Fig. 79) - in a depression formed from above by the occipital bone, the medial trapezius muscle, and laterally - by the posterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
JIAN-JIN - on the most elevated part of the shoulder girdle at the level of the middle of the distance between JIAN-YU and DA-ZHU.
DA ZHU - at the level of the interspinous space of the I-II thoracic vertebrae.
JIAN-ZHUN-SHU - in the middle of the distance between DA-ZHUI and JIAN-JIN and at the level of DA-ZHU.
NAO-SHU - under the spine of the scapula at the point of its transition to the acromial end of the scapula.
JIAN-ZHEN - at the top of the axillary fold from behind with the arm freely lowered.
GAO-HUANG - on the inner edge of the scapula at the level of the middle of the distance between the spinous processes of the IV-V thoracic vertebrae.
GE-GUAN - on the inner edge of the lower angle of the scapula at the level of the interspinous space of the VII-VIII vertebrae.
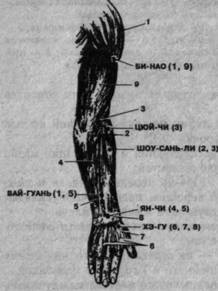
BI-HAO (Fig. 80) - at the place of attachment of the deltoid muscle to the tuberosity of the humerus of the same name.
Rice. 80. The main points of influence on the back of the hand and their effect on the muscles according to the numbering. 1 - deltoid; 2 - long radial extensor of the hand; 3- brachioradial; 4- extensor of fingers; 5 - extensorV finger; 6- interosseous;
7 - leadingI finger;
8 - short flexorI finger; 9- triceps muscle of the shoulder.
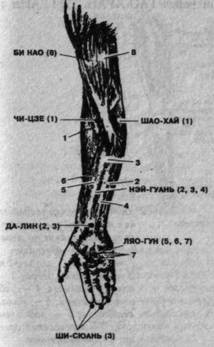
Rice. 81. The main points of influence on the front surface of the arm and their effect on the muscles according to the numbering.
1 - shoulder; 2 - long palmar; 3 - radial flexor of the hand; 4 - square pronator; 5 - deep finger flexor; 6 - superficial finger flexor; 7 - worm-like; 8 - two-headed shoulder.
QU-CHI - at the top of the fold with the arm bent as much as possible in the elbow joint.
SHOW-SAN-LI - between the muscle groups of the anterior and posterior surface of the forearm three transverse fingers (II-IV) distal to QU-CHI.
WAI-GUAN - in the middle between the ulna and the radius, three transverse fingers (II-IV) proximal to the radiocarpal joint.
YANG-CHI - in the area of the wrist joint between the tendons of the common extensor of the fingers and the extensor of the little finger proper.
HE-GU - in the first interdigital space at the level of the apex of the skin fold with the first finger adducted at the elevation of the first interosseous muscle.
SHAO-HAI (Fig. 81) - at the level of the ulnar fold outward to the ulnar side from the tendon of the biceps muscle of the shoulder.
CHI-JIE - at the level of the ulnar fold outward in the radial direction from the tendon of the biceps muscle of the shoulder.
NEI-GUAN - between the tendons of the long palmar muscle and the radial flexor of the hand, three transverse fingers (II-IV) proximal to the wrist joint.
DA-LIN - between the tendons of the long palmar muscle and the radial flexor of the hand at the level of the wrist joint.
LYAOTUN - on the palmar surface between the III and IV metacarpal bones proximal to their heads.
SHI-XUAN - on the palmar surface at the tips of the terminal phalanges of all fingers.
Influence points for relaxation and stimulation of the muscles of the gluteal region and lower extremities:
ZHI-SHI (see Fig. 79) - at the level of the interspinous space of the II-III lumbar vertebrae on the line drawn through GAO-HUANG and GE-GUAN.
ZHI-BIAN (Fig. 82) - at the level of the entrance to the sacral canal on the line drawn through GAO-HUANG, GE-GUAN and ZHI-SHI.
Rice. 82. The main points of influence on the back of the leg and their effect on the muscles according to the numbering.
1 - large gluteal;
2 - biceps thigh; 3- semitendinous; 4- middle gluteal; 5 - small gluteal; 6- popliteal; 7 - three-headed lower leg; 8- interosseous.
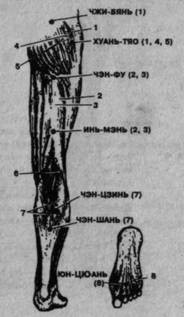
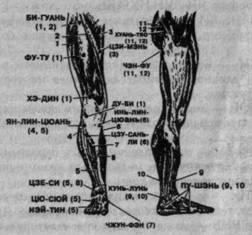
Rice. 83. The main points of influence on the front and outer surface of the leg and their effect on the muscles according to the numbering. 1- quadriceps thigh; 2 - tailor; 3- long leading; 4 - fibula; 5- long extensor of fingers; 6- gastrocnemius; 7 - anterior tibial; 8 - long extensorI finger; 9- long fibula; 10- short fibula; eleven- large gluteal; 12 - middle gluteal.
HUAN-TIAO - at the intersection of the line connecting the anterior superior iliac axis and the ischial tuberosity with the perpendicular restored from the top of the greater trochanter, or 1/3 of the distance from the top of the greater trochanter to the entrance to the sacral canal.
CHENG-FU - on the gluteal fold between the long head of the biceps femoris muscle and the semitendinosus muscle.
YIN-MEN - in the middle of the back of the thigh between the long head of the biceps femoris muscle and the semitendinosus muscle.
CHENG-JIN - in the center of the largest diameter of the lower leg between the heads calf muscle.
CHEN-SHAN - at the point of convergence of the lower edges of the abdomen of the gastrocnemius muscle.
YUN-QUAN - on the plantar surface of the foot in the interval between the II and III metatarsal bones, proximal to their heads.
BI-GUAN (fig. 83) - at the level of the perineum at the outer edge of the tailor muscle (look for the muscle when throwing legs over one leg).
FU-TU - in the middle of the distance between the upper edge of the patella and the level of the perineum on the midline of the thigh.
JI-MEN - in the lower corner of the femoral (Scarpa) triangle between the inner edge of the medial broad muscle and the front edge of the long adductor muscle of the thigh.
HE-DIN - above the middle of the upper edge of the patella with the leg bent at the knee joint.
DU-BI - at the level of the lower edge of the patella, its lateral ligaments are in a recess with the leg bent at the knee joint at an angle of 90 °.
YANG-LING-QUAN - at the site of attachment of the tendons of the long extensor of the toes and the long peroneal muscle anteriorly and downwards from the head of the fibula.
YIN-LIN-QUAN - behind the posterior edge of the tibia at the level of YANG-LIN-QUAN.
ZU-SAN-LI - lateral to one transverse II finger massaged from the lower end of the scallop of the tibia.
JE-SI - between the tendons of the long extensor of the first finger and the long extensor of the fingers at the level of the ankle joint.
QIU-XU - between the anteroinferior edge of the outer ankle and the lateral edge of the long extensor of the toes.
ZHUN-FENG - in the depression between the anteroinferior edge of the medial malleolus and the medial edge of the tendon of the anterior tibialis muscle.
NEi-Ting - in the second interdigital space at the level of the transition of the body of the main phalanges to the base.
KUN-LUN - between the posterior edge of the lateral ankle and the calcaneal (Achilles) tendon at the level of the top of the ankle.
PU-SHEN - on the outer border of the skin of the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the calcaneus under the KUN-LUN. The entire border line of the foot up to the fifth toe also belongs to the point.
ECON, Düsseldorf
(right)
(left)
Palms
(right)
![]()
(left)
reflex zones
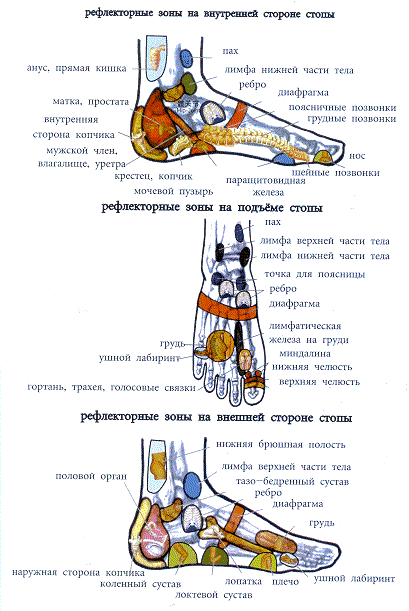
Skeleton feet
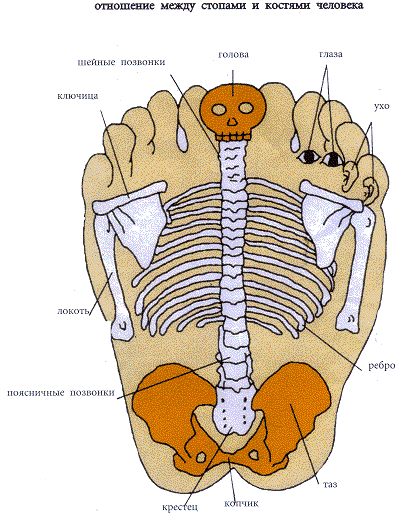
TAKE FEET IN HANDS AND...
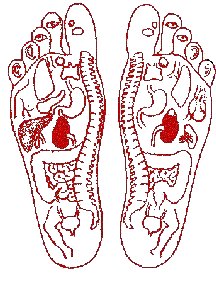
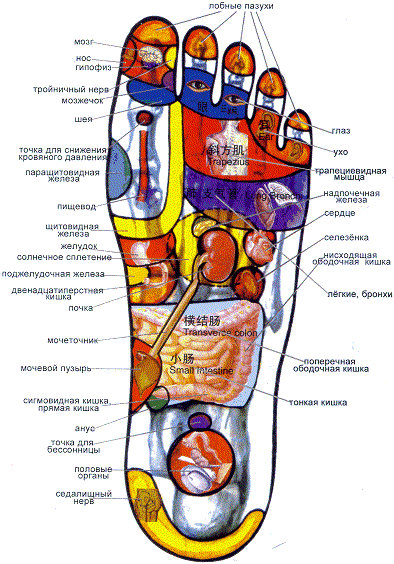
It is well known that the Motherland cannot be carried away on the soles of one's boots ... But in the East they are sure that on the soles, of course, not of boots, but of our feet, one can carry away one's own health!
The cunning Chinese have invented not only paper, a compass and gunpowder over their centuries-old history. They discovered that by massaging certain areas on the soles of the feet, one can soften or even remove pain in various parts of the body: joints, muscles, internal organs... In this way you ensure unhindered access vital energy anywhere in your body.
Remember: for headaches, you need to massage your thumb, for eye diseases - two middle fingers, for pain in the ears - the outer toes, for problems with the spine - the inside of the sole. The remaining options are clearly visible in the above diagram.
ACUPRESSURE FOR EVERYONE
Known for over five thousand years acupuncture(acupuncture) - Chinese method treatment with gold needles. IN Lately a modern analogue of such a technique appeared - electropuncture. However, not everyone knows that there is another method - acupressure. In Japan, a similar technique is called shiatsu (shea- fingers, atsu- pressure).
Acupressure treats with finger pressure.
Acupressure is a further development of acupuncture. It uses the same points (and meridians) that needles are inserted into in acupuncture, but acupressure rejects the use of metal in treatment. Instead of needles, with the same effect, the thumb and forefinger are used (you can also use your own, if available).
Pressing the fingers on the right points relieves many ailments and disorders.
Acupressure not only relieves pain, but also reduces the time of illness, eliminates the violation of the functional activity of organs, eliminates the organic consequences of neurosis (anxiety, restlessness, fear).
Everyone who knows the most important points on the body and medical indications, following the easy-to-remember rules of acupressure, will be able to help himself!
Acupressure relieves pain and treats those diseases that are caused by disorders of the nervous system, and this is every second disease in our hectic time. But above all, acupressure is reliable, safe and effective method dealing with pain - and this without any side effects. This method is especially effective when it is successfully selected and, all the more pleasant, the carrier of influence.
Acupressure does not cause the pain of a needle prick, does not cause bleeding, and eliminates the introduction of infection into the body. But most importantly, this doctor is always with you!
What are the types of points
The locations of the acupuncture and acupressure points are known exactly. They are located on 14 lines (meridians), which have long been explored. These meridians have certain names, for example, "Big heart" ("Master of the heart"), "Three-degree heater" or "Guverneur meridian", while three types of points are used on each meridian:
· "Harmonizing points" lying at the beginning and end of the meridian; their acupressure gives harmonious echoes in all organs related to this meridian;
· "Exciting point", only one on each meridian; its acupressure activates the reaction and efficiency of the organs related to this meridian;
· "calming point", also only one on each meridian; suppresses, calms, relieves a nervous state; sensations during her acupressure are most pleasant.
Enhanced acupressure of the system of the so-called “Signal (alarm) points (“Mu-points”) brings relief. Each major organ has its own signal point. Proper acupressure of this point contributes to an immediate improvement in a person’s condition and, in particular, pain reduction.
Opened in recent years whole line"Special points" related to certain ailments (diseases).
Below are the pictures key points acupressure. This can be a "Calming point" for sleep disorders, and an "Exciting point" for low blood pressure, and a "Harmonizing point" for an anxious state of general neurosis, and a "Signal point" for joint colic, and a "Special point" for impotence.
The following figures show typical dot locations. Due to the individual characteristics of the physique, the location of the points may deviate within one centimeter. By using special device, which measures the resistance of the skin, according to reduced value resistance point location is determined to the nearest millimeter. However, for acupressure, such accuracy is redundant (the size of the finger is larger). As a rule, the acupressure point reacts to strong pressure with a clear pain impulse, which makes it easier to find it in the desired area of the body.
How to influence the acupressure point?
The Chinese distinguish three degrees of influence on treatment points:
· for acute pain and primary treatment, the use of a light circular massage of the point is indicated, which is performed with the tip index finger hands. The duration of the massage is from one to five minutes.
· in chronic diseases, depending on the general condition of the patient, it is best and more reliable to use acupressure of medium strength. Multiple massage during the day is recommended, the duration of acupressure is up to thirty seconds.
· strong pressure is produced mainly with the thumb, but other options are possible.
When the desired point is found on the body, the tip of the index or thumb is touched to skin, then they begin to make circular movements with a finger, shifting the skin relative to bone or muscle tissue in a rhythm of two revolutions per second. In this case, you should pay attention to the fact that the finger constantly remains on the required point of the body.
With a symmetrical effect on acupressure points, you should be especially careful.
Contraindications
Acupressure in its simplified form cannot replace necessary medical treatment, but it can be used as an additional pain relief treatment, as well as for first aid.
Acupressure is contraindicated in:
· severe organic diseases of the heart and circulatory systems;
· during pregnancy;
· with severe overwork;
· until the cure of a skin disease at the acupressure point (suppuration, lichen, etc.)
How to do acupressure correctly?
· Sit or lie on your back.
· Watch for the absence of external stimuli (conversations of relatives, phone calls and so on)
· Take a break from everything for a while.
· Place the tip of your index finger on the desired point of the body (acupressure point).
· Lightly press on the skin and at the same time begin to make circular movements with your finger, while making sure that the finger does not leave this point of the body during movement.
· The duration of acupressure is from half a minute to five minutes.
The action always comes quickly and is felt for a long time.
Acupressure can be repeated many times throughout the day!
 Fear (depressed state). General neurosis.
Fear (depressed state). General neurosis.
Harmonizing point "Divine indifference".
Acupressure is easy up to five minutes, carried out in a sitting position with the index fingers of both hands synchronously.

Headache (frontal pain).
Calming point (symmetrical) "Hsi-san".
Light acupressure with the thumbs, always synchronous on both sides. During acupressure, the eyes should be closed.
Headache (migraine).
Calming point "Ho-gu".
Holding the point between the forefinger and thumb of the massaging hand, light rhythmic acupressure is performed with the help of the index finger. Duration - up to five minutes.
Headache (pain in the back of the head).
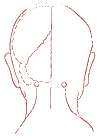 Special (symmetrical) point "Fen-khi".
Special (symmetrical) point "Fen-khi".
Strong rhythmic acupressure synchronously with both hands, can be performed with both index and thumbs hands
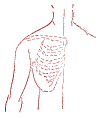 Hypertension (high blood pressure).
Hypertension (high blood pressure).
Harmonizing point "Yuan-si".
Gentle acupressure with the index finger for up to five minutes. Mandatory rest. With prolonged use, a week break should be taken.

Pain of the heart.
Calming point "Ha-ti" - "Ha-fu-(li)".
Acupressure is light, best in lying position, is carried out with the thumb, holding the brush with the index and thumb of the massaging hand. Complete peace.

Fatigue.
Exciting (special) point.
Acupressure is performed with the tip of the thumb for an hour, holding the little finger of the right hand between the index and thumb of the left hand.
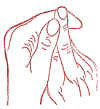 Circulatory disorders (blockage of blood vessels, poor blood flow, etc.)
Circulatory disorders (blockage of blood vessels, poor blood flow, etc.)
Exciting point "El-mu".
Pinch the middle finger of one hand between the index and thumb of the other. Acupressure is performed by pressing with an average effort with the thumbnail in the rhythm of the heartbeat alternately on both hands, changing the middle fingers in a minute.
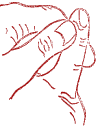 Intensive circulation. Reduced blood pressure.
Intensive circulation. Reduced blood pressure.
Exciting point "Wu-te".
Intense (to the point of pain), but short-term acupressure with the thumbnail of the other hand. With reduced pressure, it is recommended to carry out acupressure in the morning in bed.
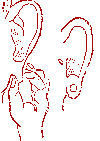 Sleep disorders.
Sleep disorders.
Special (harmonizing) point "Ha-u-san".
Light acupressure with the index finger in a state of complete rest. Action is more efficient (faster) with right side than on the left.
Age disorders (transitional age).
 Harmonizing point "Ta-neil" or "Yen-mai".
Harmonizing point "Ta-neil" or "Yen-mai".
Light acupressure with the tip of the index finger, if possible in the morning, with complete rest.
 Sexual disorders (weak erection of a man).
Sexual disorders (weak erection of a man).
Special point "Lo-si-mui".
Light pressure with index finger. Partner acupressure is preferred. A state of rest is needed.
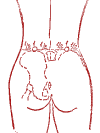
Sexual disorders (impotence of a man, coldness of a woman).
 Special point "Chli-ke".
Special point "Chli-ke".
It is carried out by alternating light and intense acupressure with the index finger. Partner acupressure is preferred. A state of rest is needed.
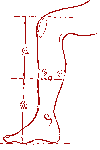
 Lumbosacral sciatica.
Lumbosacral sciatica.
Special point "Ha-te".
Strong acupressure is carried out with the help of the thumbs simultaneously on both sides. The duration of acupressure is up to two minutes.
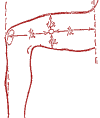
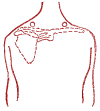 Neck sciatica. Lumbago.
Neck sciatica. Lumbago.
Harmonizing point "Fai-yuan".
Put your index fingers on the points, and squeeze the body in this place with your thumbs. Acupressure is carried out with the index fingers synchronously on both sides, at first light, then with intensification.
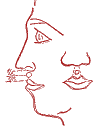
 Runny nose.
Runny nose.
1-Harmonizing point "Hi-shi". 2-Exciting point "Ku-san".
3-Calming point "Fu-san". 4-Special point "Ni-shi".
All points are symmetrical.
Acupressure is carried out in a mild form with the tips of the index fingers of both hands synchronously on both sides (one minute each pair of points). The sequence of holding 1-2-3-4. It also helps as a preventive measure.
 Flu.
Flu.
2-Exciting point "Ku-san". 3-Calming point "Fu-san".
Acupressure is carried out in a mild form with the tips of the index fingers synchronously on both sides, each point is massaged alternately for one minute.
Sore throat (inflammation, etc.)
Exciting point "Hsi-khun".
Pinch the thumb between the index and thumb of the other hand. Acupressure is carried out with medium effort, mainly by pressing the thumb, alternately changing hands. The duration is only 10 seconds.
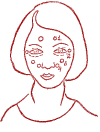
 Catarrh of the upper respiratory tract.
Catarrh of the upper respiratory tract.
Special (symmetrical) point "C-Bai".
Sit quietly. The eyes are closed. Acupressure is performed with moderate effort with the index fingers of both hands (thumbs support the chin). The duration of acupressure is 64 circular movements.

Ear ache.
Harmonizing point "Yun-Yua".
Light acupressure is performed with the index finger. Effective only in the affected ear area. Duration - until improvement.
 Sharp pain. Toothache.
Sharp pain. Toothache.
Special point "Ho-ba".
Intensive acupressure for 10 seconds with the nail of the index finger.
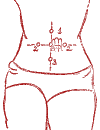
Pain of a rheumatic nature.
 Calming point.
Calming point.
Gentle but prolonged acupressure (up to 7 minutes) using the index finger alternately on both hands.
Indigestion (gastrointestinal pain).
1-Harmonizing point "Tu-she" - spasms, colic. 2-Harmonizing point "Tu-shi-(li)" - diarrhea. 3-Harmonizing point "Tu-xi"-constipation.
Only light but prolonged (patient) acupressure with index fingers, preferably while lying in bed. Point 2 requires synchronism on both sides.
Thirst.
Calming point "Yuan-tseng".
The only point of the mucous membrane of the human body, located at a distance of about one centimeter from the tip of the tongue. Acupressure is performed in the form of a light biting of the tongue at a given point with the front teeth (incisors) at a rate of 20 times per second.
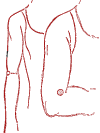 Pain in the joints.
Pain in the joints.
Harmonizing point "Yuin-hai".
Acupressure is performed with the index finger. For acute pain, only light acupressure, for chronic diseases, strong, intense acupressure. Duration - until the condition improves.
Pain in the gallbladder (colic).
Calming point "Hu-san".
Light acupressure with the index fingers of both hands at the same time. Duration - until the condition improves. Effective as a prophylactic.
Asthma. Dyspnea. Cough (smoking cessation).
Special point "Haba-ex".
Acupressure is performed in a mild form with the index finger for up to one minute. Acupressure can be repeated at any time. In the case of smoking cessation, acupressure is performed when the desire to smoke arises. In this case, a short-term, but intense (to the point of pain) acupressure is performed. It is also desirable to carry out therapy as for hypotension (low blood pressure). Dystonia.
Special point "Ha-ah-ha."
Grasping the foot with a hand, acupressure is carried out with the thumb with medium effort. Acupressure should be done in the morning and evening at long intervals. It is beneficial to carry out additional acupressure as in "Thirst" - light biting with the front teeth (incisors) of the tip of the tongue at a pace of 20 times per second.
Tired legs (overtired after running or walking for a long time).
Exciting point "Pi-in-san".
Acupressure is carried out with medium effort using the index finger, without clasping the lower leg of the massaged leg (tired leg). If necessary, acupressure is repeated.
 Dizziness.
Dizziness.
Harmonizing point "Tsyn-goal".
Strong, intense, but short-term acupressure with the index finger. If necessary, it should be combined with acupressure of the "Wu-te" (hypotension) point, carried out with the help of a thumbnail with intense pressure on the area. nail bed little finger of the other hand.
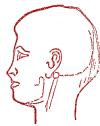
Sweating.
Special point "Ru-mai".
Light acupressure with the index finger. Duration - up to three minutes. The action is fast with acupressure on the right side, the action on the left side is much longer.
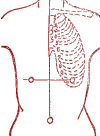 Pulmonary insufficiency. Spasms of the vagina.
Pulmonary insufficiency. Spasms of the vagina.
Exciting (symmetrical) point "Tu-li".
Light acupressure with the thumbs of both hands. Acupressure is short-term, but repeated. In female disorders, the duration of acupressure is arbitrary. A state of rest is essential.
Disorders during menstruation.
Harmonizing point.
Light acupressure, repeated many times during the "critical days". Duration - until the condition improves.
Decreased appetite.
Soothing point "Yu-pe".
Acupressure in the form of a light massage alternately on both hands when appetite occurs. Duration - 30 seconds. Impact on the point dulls the appetite and regulates (stabilizes) the metabolism.
 Stimulation of appetite.
Stimulation of appetite.
Exciting point "An-ming".
Acupressure is applied repeatedly throughout the day before meals. It is carried out rhythmically for 20 seconds of medium strength by pressing the thumbnail alternately on both hands (little fingers).
