- acute traumatic damage to the eyeball, protective and adnexal apparatus of the eye by aggressive chemicals or physical factors. An eye burn is accompanied by severe pain, loss of vision, lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva, and the appearance of blisters on the skin. Diagnosis of an eye burn is carried out taking into account the data of the anamnesis and external examination; may additionally include measurement of intraocular pressure, biomicroscopy, ophthalmoscopy. An eye burn requires immediate first aid - abundant washing of the conjunctival cavity, instillation of an anesthetic solution, application of an antibacterial ointment behind the eyelid and delivery of the patient to a hospital, where the question of further tactics is being decided.
Severe eye burns lead to necrosis of the conjunctiva and exposure of the sclera. In this case, an ulcerative defect is formed, which subsequently scars, forming adhesions between the eyelid and the eyeball. With burns of the cornea, lacrimation, photophobia, blepharospasm are noted; in severe cases - neurotrophic keratitis, clouding of the cornea. Depending on the severity of the eye burn, changes in visual function may be manifested by a slight decrease in vision or its complete loss.
With damage to the tissues of the iris and ciliary body, iritis and iridocyclitis develop. In severe eye burns, the vitreous body and lens become cloudy, the choroid and retina are damaged. Complication deep burns the eye serves the development of secondary glaucoma. In case of infection of the tissues of the eye, endophthalmitis and panophthalmitis occur. Deep chemical burns lead to perforation of the cornea and death of the eye.
Eye burns can be combined with burns to other parts of the face and body.
Diagnosis of an eye burn
Eye burns are diagnosed by history and clinical picture. When a burn injury to the eye is detected, immediate emergency care is necessary, therefore, special ophthalmological examinations are not carried out in the acute period.
In the future, to assess the degree of damage, carry out external examination eyes with eyelid lifters, determination of visual acuity, measurement of intraocular pressure, ophthalmoscopy, biomicroscopy with fluorescein staining to detect corneal ulcers, and other studies as indicated.
Treatment of eye burns
First aid for eye burns should be provided on the spot; in the future, hospitalization of the victim in an ophthalmological hospital is necessary.
Urgent measures for eye burns are abundant jet washing of the conjunctival cavity with saline or water. Independent use of neutralizing solutions is not recommended due to the possible unpredictable effect of reaction products on damaged tissues. In the first hours after the burn of the eye, the lacrimal ducts are washed, the intruded foreign bodies from the conjunctiva and cornea. Drops are instilled into the conjunctival cavity or local anesthetic ointments are applied. The introduction of tetanus toxoid to the victim is shown.
In a hospital, patients with eye burns are prescribed instillations of cytoplegic agents (atropine, scopolamine) into the eye: they can reduce pain and the likelihood of adhesion formation. In order to prevent infection, eye ointments and drops containing antibiotics (tetracycline, levomycetin, ciprofloxacin), NSAIDs are used. For eye burns, it is advisable to use lacrimal fluid substitutes. Intramuscular and parabulbar injections of antioxidants (methylethylpyridinol) are prescribed. To stimulate the regeneration of the cornea, eye gels (dialysate from the blood of dairy calves or dexpanthenol) are placed behind the eyelid. With increased IOP, local antihypertensive drugs (betaxolol, dorzolamide) are prescribed. In severe degrees of eye burns, the use of glucocorticoids (dexamethasone, betamethasone, etc.) is indicated in the form of parabulbar or subconjunctival injections.
From non-drug methods for eye burns, physiotherapy and eyelid massage are used.
Surgical tactics in case of eye burns, it is very variable and is determined by the nature and degree of damage to the eye tissues. If chemical reagents enter the anterior chamber of the eye, it is necessary to perform corneal paracentesis and remove the infiltrated substances.
With the threat of loss of an eye in early dates after an eye burn, surgical interventions can be performed on the eyelids or the eyeball - necrectomy of the conjunctiva and cornea, vitrectomy, plastic surgery of the conjunctival cavity, early keratoplasty, etc.
In the future, it may be necessary to perform plastic surgery on the eyelids - correction of inversion or eversion of the eyelid, elimination of ptosis, restoration of eyelashes with trichiasis, surgery post-burn cataracts, etc. With the formation of corneal scars in the delayed period, layer-by-layer or penetrating keratoplasty is performed; with the development of secondary glaucoma - antiglaucomatous surgery.
Forecast and prevention of eye burns
The prognosis for eye burns is determined by the nature and severity of the injury, the timing of the provision of specialized assistance, the correctness of the drug therapy. The outcome of severe eye burns, as a rule, is entropion, the formation of a walleye, infection of the conjunctival cavity, atrophy of the eyeball, and a significant degree of visual function reduction.
According to experts, about 90% of cases of eye burns can be prevented. Therefore, the prevention of eye burns, first of all, requires compliance with safety precautions when handling chemical and flammable substances, household chemicals; use of protective goggles with light filters. Patients with eye burns require follow-up by an ophthalmologist for at least 1 year after injury.
Impaired transparency of the cornea
Decrease, narrowing of visual fields
Increase or decrease in intraocular pressure
With radiation burns of the eyes, some of these symptoms may be absent, since infrared or laser beams damage mainly the cells and choroid of the eye.
It should be remembered that immediately after an injury it is not always possible to determine the severity of eye damage. A patient with thermal eye burns, regardless of the severity of the lesion, must be urgently taken to the hospital and shown to a specialist. Very often, the prognosis of the disease directly depends on the speed and volume of adequate medical care.
Classification of eye burns
There is no single generally accepted classification of eye burns. Eye burns are classified according to the type of damaging factor, according to the localization of damage, according to the depth of the lesion.
According to localization, burns, choroid are isolated.
Depending on the depth of damage, 4 degrees of severity of eye burns are distinguished (according to Pole). The lightest is a first-degree burn, the outcome of such a lesion is favorable in almost 100% of cases. Eye burns of a more severe (II - IV) degree are always treated in a hospital, the consequences of such a lesion can be extremely severe.
Thermal eye burns
Thermal eye burns occur when exposed to extremely high or low temperatures, including when exposed to hot liquid, fire, steam, incandescent or burning solid particles, as well as dry ice, cryogenic liquids or liquefied gases. Such burns are usually localized in the anterior parts of the eyes, damage to the deep parts of the eyes is observed only in case of severe burns.
If an eye burn occurs, if possible, remove traces of the traumatic substance from the skin around the eyes and rinse the eyes with a weak stream of water. An ointment with an antiseptic or antibiotic (for example,) is applied to the skin around the eye, the same ointment is placed behind the eyelid. An aseptic bandage is carefully applied to the eye, while rubbing or scratching the eyes is strictly prohibited. The patient is urgently hospitalized for specialized care.
Chemical burns to the eyes
Chemical burns of the eyes occur most often under the influence of acids or caustic alkalis; in everyday life, eye burns may occur when crystals of potassium permanganate, ammonia, iodine solution, lime, household chemicals and various cosmetic products.
A feature of chemical burns is the duration of exposure to the damaging factor. So, when alkali gets into the eye, it damages not only the tissues directly at the point of contact, but is able to penetrate into the deep-lying parts of the eye.
In case of contact with the eyes of chemicals, it is necessary to immediately rinse the eyes with a weak stream of water (for at least 10-15 minutes, until the traces of this substance completely disappear from the eye). Antiseptic eye drops (for example,) are instilled into the conjunctival sac of the eye, the skin around the eye is lubricated with antiseptic ointment, after which the affected eye is covered with an aseptic bandage and the victim is urgently sent for examination to an ophthalmologist.
Radiation eye burns (welding)
Radiation damage to the eyes has some features depending on the type of damaging factor. Radiation burns occur when exposed to shortwave ( ultra-violet rays) and long-wave (infrared rays) radiation. Most often, such damage occurs after a visit to the solarium, on ski resorts("snow blindness"), as well as electric welders.
Radiation burns of the eyes do not appear immediately, but after a few hours (on average, after 4 to 6 hours). Typical complaints in case of radiation damage to the eyes are strong, photophobia, a sharp deterioration in vision due to damage to the retina. As in the case of other eye burns, with radiation damage, the patient needs immediate help. Pain-relieving eye drops (""), corticosteroids ("", ""), drugs to relieve local edema and oil solutions of vitamins (""), remedies (, "Levomitsetin") are used.
First aid and treatment of eye burns
Regardless of the type of eye burn, first aid for eye burns should be aimed at eliminating the damaging factor ( chemical, temperature or radiation), instillation of antibacterial drops (, "Albucid", "Levomycetin", "Sulfacyl Sodium", etc.) and laying ointments). This is done to prevent secondary infection of damaged eye tissue. Further, as a rule, a sterile bandage is applied to the eye and the victim is taken to a specialized medical institution(by passing transport or by ambulance car).
Regardless of what exactly caused the burn, you should immediately contact a specialist. The sooner help is provided and treatment is prescribed, the sooner it will be possible to avoid various kinds of complications. As a restorative treatment after removing the pain syndrome and disinfecting the mucous membrane of the eye, doctors prescribe eye gels. In ophthalmic practice, there are special means for regeneration (recovery) and preservation of the functions of the cells of the cornea and conjunctiva, which prevent the development of complications in the most early signs tissue damage to the surface of the eye. One of these drugs is Korneregel, a dexpanthenol-based eye gel that heals the cornea and conjunctiva, and also prevents the deterioration in the quality of vision that can be caused by complications. The gel eliminates pain, swelling and redness due to the reparative action, and the carbomer, which is part of its composition, provides long-term hydration, relieving discomfort.
Eye burn - damage to the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea or deeper structures of the eye when exposed to chemicals, heat, certain types of rays.
When exposed to aggressive chemicals or high temperatures, a person's eyelids shrink reflexively, protecting the surface of the eyeball from burning. In some cases, only the eyelids may be damaged, but with very high temperature the eye itself may be damaged. The severity of the injury, the intensity of the pain syndrome, appearance eyes and eyelids depend on the depth of the eye burn.
Symptoms
With this type of damage, a person immediately feels a burning pain in the eye and itching, there is lacrimation, an acute fear of light and significant loss of vision. The chemical and thermal type of exposure is often accompanied by reddening of the eyelids, as well as clouding of the corneas, the appearance of blisters and films, which are easily removed with minor injuries, and are not removed at all with third and fourth degree burns.
In especially difficult cases, ulcers and scars, necrosis of the tissues of the eyeball and eyelids, a change in their shape and swelling are observed. The features of such an injury as a burn of the retina of the eye consist in symptoms that have their own distinct character: first of all, there is a significant clouding of the cornea and tissue necrosis, as well as glaucoma. A thorn appears on the eye, because the retina in its appearance begins to resemble frosted glass. These processes are accompanied by loss of vision, which is quite difficult or completely impossible to return with severe burns. The consequences of the disease can be a wide variety of complications, ranging from scars, ulcers, slight loss of vision to complete blindness.
Source narmed24.ru
signs
Complaints of pain in the affected eye, photophobia, decreased vision. Objectively marked spasm of the eyelids, swelling of the skin of the eyelids and conjunctiva.
First aid
First aid for eye burns is as much as possible fast removal damaging substance. If a burning particle gets into the eye, despite the spasm, one should try to open the eye and remove it. First aid for eye burns by a chemical agent, acid or alkali, consists in immediate and abundant washing of the eyes with water. Pain medication may be given until the ambulance arrives.
Source neboleem.net
Urgent Care
First aid for chemical eye burns is to wash the conjunctival sac with plenty of water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
If possible, in case of alkali burns, it is better to rinse the damaged eye with a 2–4% solution. boric acid, and in cases of burns with an aniline pencil - a 5% solution of ascorbic acid.
The particles of the chemical remaining in the conjunctival sac after anesthesia with a 1% solution of dicaine are removed with a wet swab. Subsequently, the conjunctival cavity is injected disinfectant solutions and ointments.
Source medkurs.ru
Treatment
First aid for eye burns should be provided on the spot; in the future, hospitalization of the victim in an ophthalmological hospital is necessary.
Urgent measures for eye burns are abundant jet washing of the conjunctival cavity with saline or water. Independent use of neutralizing solutions is not recommended due to the possible unpredictable effect of reaction products on damaged tissues. In the first hours after an eye burn, the lacrimal ducts are washed, and foreign bodies that have invaded from the conjunctiva and cornea are removed. Drops are instilled into the conjunctival cavity or local anesthetic ointments are applied. The introduction of tetanus toxoid to the victim is shown.
In a hospital, patients with eye burns are prescribed instillations of cytoplegic agents (atropine, scopolamine) into the eye: they reduce pain and the likelihood of adhesions. In order to prevent infection, eye ointments and drops containing antibiotics (tetracycline, levomycetin, ciprofloxacin), NSAIDs are used. For eye burns, it is advisable to use lacrimal fluid substitutes. Intramuscular and parabulbar injections of antioxidants (methylethylpyridinol) are prescribed. To stimulate the regeneration of the cornea, eye gels (actovegin, solcoseryl or dexpanthenol) are placed behind the eyelid. With increased IOP, local antihypertensive drugs (betaxolol, timolol, dorzolamide) are prescribed. In severe degrees of eye burns, the use of glucocorticoids (dexamethasone, betamethasone, etc.) is indicated in the form of parabulbar or subconjunctival injections.
From non-drug methods for eye burns, physiotherapy and eyelid massage are used.
Surgical tactics for eye burns is very variable and is determined by the nature and degree of damage to the eye tissues. If chemical reagents enter the anterior chamber of the eye, it is necessary to perform corneal paracentesis and remove the infiltrated substances.
With the threat of eye loss in the early stages after an eye burn, surgical interventions on the eyelids or the eyeball can be performed - necrectomy of the conjunctiva and cornea, vitrectomy, plastic surgery of the conjunctival cavity, early keratoplasty, etc.
In the future, it may be necessary to perform plastic surgery on the eyelids - correction of inversion or eversion of the eyelid, elimination of ptosis, restoration of eyelashes in trichiasis, surgical treatment of post-burn cataracts, etc. If corneal scars form in the delayed period, layered or penetrating keratoplasty is performed; with the development of secondary glaucoma - antiglaucomatous surgery.
Source krasotaimedicina.ru
Welding
Radiation damage to the eyes has some features depending on the type of damaging factor. Radiation burns occur when exposed to short-wave (ultraviolet rays) and long-wave (infrared rays) radiation. Most often, such injuries occur after visiting a solarium, in ski resorts (“snow blindness”), as well as in electric welders.
Radiation burns of the eyes do not appear immediately, but after a few hours (on average, after 4 to 6 hours). Typical complaints in case of radiation injuries of the eyes are severe pain in the eyes, lacrimation, photophobia, a sharp deterioration in vision due to damage to the retina. As in the case of other eye burns, with radiation damage, the patient needs immediate help. Pain-relieving eye drops ("Inocaine"), corticosteroids ("Dexamethasone", "Hydrocortisone eye ointment"), preparations to relieve local edema and oil solutions of vitamins ("VitA-Pos"), antibacterial agents ("Levomycetin", "Floxal" ).
Source proglaza.ru
Chemical
They occur when acids and alkalis accidentally get behind the eyelids in the form of solutions, and sometimes in the form of powders. IN rare cases chemical burns of the eyes arise from the mistaken instillation of solutions of acids or alkalis, mistaken for eye drops. In practice, this is most often ammonia, from which, as a rule, the eye goes blind. Therefore, ammonia and other alkalis, as well as acids, should not be dispensed in the same bottles in which eye drops are sold. It is also important for patients using eye drops and ammonia to label the latter with red or other bright adhesive tape so as not to be confused with eye drops.
Diagnostics. Complaints of severe pain in the eye, photophobia, a sharp deterioration in vision. Objectively, a pronounced mixed injection, clouding of the cornea are determined.
First aid. If a powdered chemical gets behind the eyelids, it is necessary to remove it with dry cotton wool wound around a match, and only after that you can start washing the eye. For burns caused by liquid chemicals, eye rinsing should be started as soon as possible. It is the speed of the beginning of the washing that decides the fate of the eye. You can wash the eye under a tap with a loose ball of cotton wool, which is moistened with water, and, without squeezing, spend it along the edges of the eyelids from the temple to the nose for 10-15 minutes. If it is known that the burn was caused by alkali, a 2% solution of boric acid can be used for washing, and if the eye is burned with acid, then a soda solution is used for washing. You can also rinse from a rubber balloon, using an eye glass bath, etc. In no case should you limit yourself to rinsing for 1-2 minutes, especially for burns with a powdered chemical. After 10-15 minutes of rinsing, 0.25% -0.5% dicaine solution, 4% - 5% solution of novocaine, grimecaine or lidocaine, 10% -30% solution of sodium sulfacyl (albucid) and 0.2 % solution of chloramphenicol. On the way, with pain in the eye, you can once again give an analgesic tablet inside. Hospitalization in an eye hospital.
Source glazmed.ru
Solar
Most often, sunburn occurs on the face. Because this part of the body is quite difficult to close from the sun's rays. But, at the same time, it is the skin of the face that is most resistant to infrared radiation. Therefore, facial sunburn rarely presents with extreme redness, blistering, and peeling.
Most often, a sunburn of the face is accompanied by symptoms such as:
burning sensation;
slight hyperemia;
appearance age spots;
dry skin;
feeling of tightness.And now let's talk about how first aid should be provided for sunburn. We have already discussed above that the main danger in this condition is tissue breakdown and dryness. skin. This is what causes the appearance of blisters, a burning sensation and subsequent rejection of the damaged epidermis.
Therefore, it is important to do the following:
reduce the temperature in the affected areas - cold compresses or ice wrapped in rags will help here;
ensure sufficient hydration - use olive oil;
prevent tissue breakdown - take any ointment that contains a regenerating agent.
Inside, you can be advised to take an aspirin tablet to reduce blood viscosity and reduce inflammation. The victim needs to drink a large number of water and be in the shade. Preferably within the first 3 days after receiving sunburn don't go straight Sun rays. In case of sunburn of the eyes, 2 drops of albucid should be instilled into each eye and urgently seek help from an ophthalmologist.
Ointment and remedy for sunburnIf you want to choose an ointment for sunburn, then pay attention to the following types:
methyluracil;
heparin;
lorinden C;
containing diclofenac, ortofen.But the best remedy from solar burns - this spray panthenol. It contains everything you need to moisturize the skin, regenerate cells and reduce pain.
Source auroum.ru
acid
An acid burn has the same effect as a thermal eye burn. The depth of exposure depends entirely on the time of contact and the concentration of the acid.
The cornea is affected in the zone of acid exposure, where an area of necrosis appears.
Necrosis takes place as a coagulation process. Necrotic tissue is limited from healthy.
Source hvatit-bolet.ru
Acid eye burns are chemical burns with a pH below 7. Acid burns to the eyes usually result in less grave consequences compared to burns caused by alkali. Acid does not penetrate as deeply into the eye as alkali, with the exception of hydrofluoric acid (HF). Acid usually damages only the anterior parts of the eye, however, in this case, a pronounced burn of the cornea can lead to blindness.
The most common eye burns are sulfuric, sulphurous, hydrochloric, nitric, nitrite, acetic, chromic and hydrofluoric acids. In everyday life, these acids are found in glass polish, vinegar, acetone, etc.
First aid for chemical eye burns consists in abundant washing of the conjunctival sac with water or a weak (1:5000) solution of potassium permanganate. If possible, in case of alkali burns, it is better to rinse the damaged eye with a 2-4% solution of boric acid or a 0.1% solution acetic acid, and in case of burns with an aniline pencil - 3-5% tannin solution or 5% ascorbic acid solution.
The particles of the chemical remaining in the conjunctival sac after drip anesthesia with a 0.25-0.5% solution of dicaine are removed with a wet swab, tweezers or a needle. If it is difficult to remove pieces of lime from the surface tissues of the eye, frequent (every 30-60 minutes) instillations of EDTA into the conjunctival sac, which forms a soluble, easily washed out complex with calcium compounds, are advisable.
After release from the chemical, disinfectant solutions and ointments are injected into the conjunctival cavity. They are used for thermal eye burns. Anti-tetanus serum is administered according to Bezredka (1500 AU). Further treatment of the patient is carried out in a hospital. This treatment should contribute to the maximum preservation of the optical properties of the cornea, the suppression of autoimmune reactions, the prevention of excessive vascularization, conjunctival adhesions, iritis, iridocyclitis, secondary glaucoma and cataracts.
Source medee.ru
quartz lamp
As with any injury, great importance has first aid. An eye burn with a quartz lamp is accompanied by certain symptoms, depth and characteristics of tissue damage, depending on the time spent in the quartz room, as well as the placement of the eyes relative to the lamp. In addition, such burns are distinguished from other eye lesions (for example, by ultraviolet radiation). They can be varying degrees, and both the cornea and the conjunctiva, eyelids can be affected.
Light burns of the eyelids are accompanied by relatively mild pain, swelling and redness. This is usually observed if the person did not directly look at the lamp, or did not face it for a long time. Light burns of the conjunctiva are most often isolated. That is, apart from this tissue, nothing suffers. This happens when looking at the lamp for a short time. And it manifests itself after a few hours and is accompanied by moderate redness, the appearance of lacrimation and pain when contemplating light. A burn with a quartz lamp is manifested by lacrimation, photophobia and eye pain. The eye can be opened for a few seconds, then it reflexively closes. Eyelids are difficult to unclench.
Burn moderate characterized by damage not only to the eyelids, but also to the cornea and conjunctiva.
Severe burns occur, as a rule, with thermal damage to the rays of a quartz lamp, if it was close to the face. The lesions appear as yellow or dark gray crusts on the eyelids, and the eyes cannot be opened. The eyelids swell, redden, blisters appear, severe pain accompanies the opening of the eyes. Symptoms of a burn of the conjunctiva of the middle and severe degree appear much earlier. In this case, the eye turns very red, the victim complains of severe pain accompanied by lacrimation and photophobia.
Source mykozha.ru
It is worth emphasizing once again that seeking help in case of this kind burns should be done as quickly as possible. If this is not done or postponed indefinitely, it will suddenly heal on its own, and also if you provide the wrong help, then get ready for the worst. Don't expect everything to work out. Therefore, we repeat once again - this is important! - you need to contact not just an emergency room, but a narrow specialist, a good professional in his field immediately!
So, firstly, we will describe those actions that in no case should be taken if the eyes are still burned by a quartz lamp.
IT IS FORBIDDEN:
Press and rub the burned eye, even if you really want to.
Trying to wash your eyes - just water will not work, and the quality of our water has long been known.
Use a cotton bandage on the affected eye - it will create a greenhouse effect, but you can’t warm the eye, it is already more than warm.
The next thing to do immediately in case of a burn with a quartz lamp is to provide first aid.
First you need to take the victim to a dark room, or at least where there are tight curtains. This is necessary because in a person who has received such a burn, the eyes become very sensitive to light: it hurts not only to look at the light, but also to open your eyes.
Under the eyelid, it is advisable to lay an antibacterial ointment, if one is at hand, which is unlikely.
If the pain is very annoying, then you can offer the victim an anesthetic - oral or intramuscular.
Apply dry ice to the eye or, if this is not available, you can wrap the frozen contents of your freezer in a bag.
If the pain is still bothering, then immediately consult a doctor.
SO, THIS IS WHAT WE CAN DO:
Reassure the burnt person and take them to a darkened room.
Explain to the victim what absolutely cannot be done.
Deliver the patient as soon as possible to a special emergency room.
It is necessary to clean the damaged area around the eyes of contamination.
Give pain medication.
You can apply ice, but be careful not to create pressure on the sore eye. Between the eye and the ice, it would be better to lay a clean, thin bandage.
The last and most important thing to do quickly after an eye burn with a quartz lamp is to provide inpatient treatment in a hospital.Eye diseases, and in this article we will talk about eye burns with a quartz lamp, require some treatment. Let's look at what kind of treatment may be required.
Source ozrenii.com
ultraviolet
Burns, which were the result of exposure to radiant energy, occur under the influence of solar radiation, when the atmosphere weakly delays UV radiation. Most often, such burns can be obtained in mountainous areas or in the tundra. It should be noted that they are called “snow ophthalmia”, and they are also called snow or mountain blindness. Sometimes an eye burn with ultraviolet light can be obtained due to long stay in the bright sun, as well as from artificial sources of UV - radiation (electric welding, quartz lamps and other devices). Photophthalmia, which is a consequence of radiation sources ultraviolet radiation, is called electrophthalmia, i.e. thermal burn of the eyes.
Symptoms of eye burns from ultraviolet rays
5 to 7 hours after UV exposure, the victim develops blepharospasm, sharp pain in the eyes, photophobia and lacrimation, as well as redness of the conjunctiva. In especially severe cases, superficial vesicles and opacities appear on the cornea. Hyperemia and edema develop on the mucous membrane of the eyes, the cornea grows dull. With the help of a biomicroscope, edema of the epithelium is detected (sometimes its rejection). There is a decrease in the sensitivity of the cornea. In this condition, when making a diagnosis, it is necessary to consider the fact of possible ultraviolet radiation.
Source hirurgs.ru
First aid for ultraviolet burns:
Being in a dark room;
Cold lotions from water with ice;
Cool compresses from sleeping tea;
Special eye drops such as "artificial tear".
If the pain is unbearable, and the accident occurred on a hike or where it is difficult to get medical care, you can drip novocaine or dicaine as an anesthetic.
As a rule, even without special treatment, within a few days, the symptoms of sunburn of the eyes pass without a trace and you can return to your usual life.
Today there are a number of "harmful" professional jobs, during which special care must be taken. This should include the work of a welder, during which it is possible to injure the organs of vision. If you do not use special protective equipment and look at flying sparks, then this is fraught with such a complication as a burn of the mucous membrane of the eye. In this case, a number of unpleasant symptoms occur - pain, redness, burning. Special drops can help to overcome it.
The eyes are a vulnerable human organ that needs to be protected. If mistakes were made during the welding work, then this negatively affects the cornea of the eye, a burn. As a result, the following clinical picture is formed:
- increased tearing;
- photophobia;
- opening the eyes leads to sharp pain;
- redness;
- swelling and.
If the presented symptomatology takes place, then this is a reason for acquiring special eye drops.
Features of drugs
 If you cannot seek help from an ophthalmologist, you can cope with the symptoms of eye damage during welding with the help of eye drops. Today, several types of these drugs are produced:
If you cannot seek help from an ophthalmologist, you can cope with the symptoms of eye damage during welding with the help of eye drops. Today, several types of these drugs are produced:
- Vasoconstrictor. Due to these medications, it is possible to completely or partially get rid of the resulting clinical picture.
- . Thanks to them, you can freeze the pain syndrome, reduce itching and inflammation.
- Antibacterial. These drops reduce unpleasant manifestations due to the fact that they kill harmful bacteria that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process.
List of drugs
Painkillers
First of all, it is necessary to stop the pain syndrome of the eye that arose as a result of welding. To do this, use drops with a local anesthetic effect. The most effective are:
- Lidocaine. Apply 2% solution.
- Inocaine. This drug allows you to reduce pain, while not leading to the development of irritation of the conjunctiva and cornea, which cannot be said about the previous medication.
The pain can be removed after 30 seconds after the application of the selected drug.
To relieve pain in the eyes after welding, you should use these medicines only on the recommendation of a doctor. If you use drops uncontrollably often, this will lead to the development of eye erosion.
Antibiotics
As soon as it was possible to stop the pain syndrome, then it is worth taking care that the infection did not penetrate into the wound channels. To do this, it is necessary to use drops with an antibacterial effect. The following drugs remain effective:

Drops with an antibacterial effect have a quick positive result. At the same time, a decrease in swelling and inflammation is achieved, which rapidly develop in the cells of the cornea and retina after receiving a burn.
Vasoconstrictor
With the help of these drugs, you can stop the swelling of the cornea visual organ, inflammation and redness. Drops such as Prokulin and Vizoptin remain very effective today.. They should be dripped 1 drop 3 times a day.
To be noticeable positive effect, it is sufficient to apply vasoconstrictor drops within 3 days.
Recovery drops
At the last stage of treatment, it is necessary to eliminate all the consequences of the injury. To do this, it is effective to use drops with a restorative effect.
It is worth using drops to treat a burn only if they alternate. This will give you the best and fastest results.
 Thus, in turn, you can use the following drugs:
Thus, in turn, you can use the following drugs:
- . This drug has a tonic effect on the vessels of the eyes. When using drops, it is possible to resolve the hemorrhage in the mucous membrane of the visual organ, as well as normalize blood flow in the vessels.
- Derinat. This tool is suitable for the quick and scarless removal of burns resulting from welding. Due active components can speed up the recovery of damaged tissues.
- Vitasik. The action of this drug is aimed at improving the healing of manifestations of the internal environment of the visual organ.
Apply funds sequentially with an interval of 1 hour. This will allow you to optimally affect the affected area.
For getting maximum effect from the applied drops, you should use the following recommendations:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap.
- Using bottled water, rinse eyes thoroughly.
- Examine the mucous membrane of the eye in front of a mirror. If metal particles are noticeable there, then you can get rid of them with a sterile cotton swab. Do this gently, without putting pressure on the eye.
- Soak a cotton swab in water and apply to the eye for a couple of minutes.
- After the done activities, you can use the prescribed eye drops.
Video
conclusions
The work of a welder is quite dangerous because you can get a burn of the mucous membrane of the eye. If you don't start timely treatment, then this is fraught with various complications, including visual impairment. And although all drugs are very effective, they should be used only after consulting a specialist, so as not to get the opposite effect.
Also read about which drops are used and.
15-10-2012, 06:52
SYNONYMS
Chemical, thermal, radiation damage to the eyes.
ICD-10 CODE
T26.0. Thermal burn of the eyelid and periorbital region.
T26.1. Thermal burn of the cornea and conjunctival sac.
T26.2. Thermal burn leading to rupture and destruction of the eyeball.
T26.3. Thermal burns of other parts of the eye and its adnexa.
T26.4. Thermal burn of the eye and adnexa of unspecified localization.
T26.5. chemical burn eyelid and periorbital region.
T26.6. Chemical burn of the cornea and conjunctival sac.
T26.7. Chemical burn leading to rupture and destruction of the eyeball.
T26.8. Chemical burn of other parts of the eye and its adnexa.
T26.9. Chemical burn of the eye and adnexa of unspecified localization.
T90.4. Sequelae of an eye injury in the periorbital region.
CLASSIFICATION
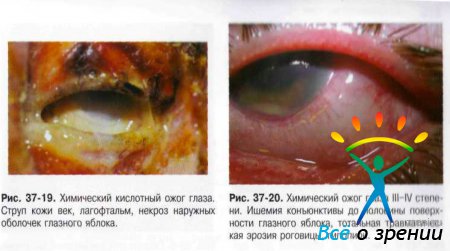
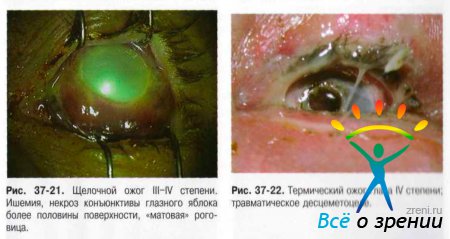
- I degree- hyperemia of various parts of the conjunctiva and the limbus zone, superficial erosion of the cornea, as well as hyperemia of the skin of the eyelids and their swelling, slight swelling.
- II degree b - ischemia and superficial necrosis of the conjunctiva with the formation of easily removable whitish scabs, clouding of the cornea due to damage to the epithelium and superficial layers of the stroma, the formation of blisters on the skin of the eyelids.
- III degree- necrosis of the conjunctiva and cornea to deep layers, but not more than half of the surface area of the eyeball. The color of the cornea is "matte" or "porcelain". Changes in ophthalmotonus are noted in the form of a short-term increase in IOP or hypotension. Perhaps the development of toxic cataracts and iridocyclitis.
- IV degree- deep lesion, necrosis of all layers of the eyelids (up to charring). Damage and necrosis of the conjunctiva and sclera with vascular ischemia on the surface of more than half of the eyeball. The cornea is "porcelain", a tissue defect over 1/3 of the surface area is possible, in some cases perforation is possible. Secondary glaucoma and severe vascular disorders - anterior and posterior uveitis.
ETIOLOGY
Conventionally, chemical (Fig. 37-18-21), thermal (Fig. 37-22), thermochemical and radiation burns are distinguished.

CLINICAL PICTURE
Common signs of eye burns:
- the progressive nature of the burn process after the cessation of exposure to the damaging agent (due to metabolic disorders in the tissues of the eye, the formation of toxic products and the occurrence of an immunological conflict due to autointoxication and autosensitization by the post-burn period);
- a tendency to recurrence of the inflammatory process in the choroid at different times after receiving a burn;
- a tendency to the formation of synechia, adhesions, the development of massive pathological vascularization of the cornea and conjunctiva.
- Stage I (up to 2 days) - the rapid development of necrobiosis of the affected tissues, excessive hydration, swelling of the connective tissue elements of the cornea, dissociation of protein-polysaccharide complexes, redistribution of acid polysaccharides;
- Stage II (2-18 days) - manifestation of pronounced trophic disorders due to fibrinoid swelling:
- Stage III (up to 2-3 months) - trophic disorders and vascularization of the cornea due to tissue hypoxia;
- Stage IV (from several months to several years) - a period of scarring, an increase in the amount of collagen proteins due to an increase in their synthesis by corneal cells.
DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnosis is based on history and clinical presentation.
TREATMENT
Basic principles of treatment of eye burns:
- providing emergency care aimed at reducing the damaging effect of a burn agent on tissues;
- subsequent conservative and (if necessary) surgical treatment.
Washing is not carried out with a thermochemical burn if a penetrating wound is found!
Surgical interventions on the eyelids and the eyeball in the early stages are carried out only in order to preserve the organ. Vitrectomy of burnt tissues is performed, early primary (in the first hours and days) or delayed (in 2-3 weeks) blepharoplasty with a free skin flap or a skin flap on a vascular pedicle with a simultaneous transplantation of automucosa on inner surface eyelids, vaults and on the sclera.
Planned surgical interventions on the eyelids and the eyeball with the consequences of thermal burns, it is recommended to carry out 12-24 months after the burn injury, since against the background of autosensitization of the body, allosensitization to the graft tissues occurs.
For severe burns, 1500-3000 IU of tetanus toxoid should be injected subcutaneously.
Treatment of stage I eye burns
Prolonged irrigation of the conjunctival cavity (within 15-30 minutes).
Chemical neutralizers are used in the first hours after the burn. In the future, the use of these drugs is impractical and may have a damaging effect on the burned tissue. For chemical neutralization, the following means are used:
- alkali - 2% solution of boric acid, or 5% solution citric acid, or 0.1% lactic acid solution, or 0.01% acetic acid:
- acid - 2% sodium bicarbonate solution.
NSAIDs
H1 receptor blockers: chloropyramine (orally 25 mg 3 times a day after meals for 7-10 days), or loratadine (orally 10 mg 1 time per day after meals for 7-10 days), or fexofenadine (orally 120-180 mg 1 time per day after meals for 7-10 days).
Antioxidants: methylethylpyridinol (1% solution of 1 ml intramuscularly or 0.5 ml parabulbarno 1 time per day, for a course of 10-15 injections).
Analgesics: metamizole sodium (50%, 1-2 ml intramuscularly for pain) or ketorolac (1 ml for pain intramuscularly).
Preparations for instillation into the conjunctival cavity
In severe conditions and early postoperative period the multiplicity of instillations can reach 6 times a day. As the inflammatory process decreases, the duration between instillations increases.
Antibacterial agents: ciprofloxacin (eye drops 0.3%, 1-2 drops 3-6 times a day), or ofloxacin (eye drops 0.3%, 1-2 drops 3-6 times a day), or tobramycin 0.3% ( eye drops, 1-2 drops 3-6 times a day).
Antiseptics: picloxidine 0.05% 1 drop 2-6 times a day.
Glucocorticoids: dexamethasone 0.1% (eye drops, 1-2 drops 3-6 times a day), or hydrocortisone (eye ointment 0.5% for the lower eyelid 3-4 times a day), or prednisone (eye drops 0.5% 1-2 drops 3-6 times a day).
NSAIDs: diclofenac (orally 50 mg 2-3 times a day before meals, course 7-10 days) or indomethacin (orally 25 mg 2-3 times a day after meals, course 10-14 days).
Midriatics: cyclopentolate (eye drops 1%, 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day) or tropicamide (eye drops 0.5-1%, 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day) in combination with phenylephrine (eye drops 2 5% 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days).
Corneal regeneration stimulators: actovegin (eye gel 20% for the lower eyelid, one drop 1-3 times a day), or solcoseryl (eye gel 20% for the lower eyelid, one drop 1-3 times a day), or dexpanthenol (eye gel 5% for the lower eyelid 1 drop 2-3 times a day).
Surgery: sectoral conjunctivotomy, corneal paracentesis, conjunctival and cornea necrectomy, genonoplasty, corneal biocoverage, eyelid surgery, layered keratoplasty.
Treatment of stage II eye burns
Groups of drugs are added to the ongoing treatment, stimulating immune processes, improving the utilization of oxygen by the body and reducing tissue hypoxia.
fibrinolysis inhibitors: aprotinin 10 ml intravenously, for a course of 25 injections; instillation of the solution into the eye 3-4 times a day.
Immunomodulators: levamisole 150 mg 1 time per day for 3 days (2-3 courses with a break of 7 days).
Enzyme preparations: systemic enzymes 5 tablets 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals, drinking 150-200 ml of water, the course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Antioxidants: methylethylpyridinol (1% solution of 0.5 ml parabulbarno 1 time per day, for a course of 10-15 injections) or vitamin E (5% oil solution, inside 100 mg, 20-40 days).
Surgery: layered or penetrating keratoplasty.
Treatment of stage III eye burns
The following are added to the treatment described above.
Short-acting mydriatics: cyclopentolate (eye drops 1%, 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day) or tropicamide (eye drops 0.5-1%, 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day).
Antihypertensive drugs: betaxolol (0.5% eye drops, twice daily) or timolol (0.5% eye drops, twice daily) or dorzolamide (2% eye drops, twice daily).
Surgery: keratoplasty according to emergency indications, antiglaucoma operations.
Treatment of stage IV eye burns
The following are added to the ongoing treatment.
Glucocorticoids: dexamethasone (parabulbarno or under the conjunctiva, 2-4 mg, for a course of 7-10 injections) or betamethasone (2 mg betamethasone disodium phosphate + 5 mg betamethasone dipropionate) parabulbarno or under the conjunctiva 1 time per week 3-4 injections. Triamcinolone 20 mg once a week 3-4 injections.
Enzyme preparations in the form of injections:
- fibrinolysin [human] (400 IU parabulbarno):
- collagenase 100 or 500 KE (the contents of the vial are dissolved in 0.5% procaine solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution or water for injection). It is administered subconjunctivally (directly into the lesion: adhesion, scar, ST, etc. using electrophoresis, phonophoresis, and also applied to the skin. Before use, the patient's sensitivity is checked, for which 1 KE is injected under the conjunctiva of the diseased eye and observed for 48 hours. In the absence of an allergic reaction, treatment is carried out for 10 days.
Non-drug treatment
Physiotherapy, eyelid massage.
Approximate periods of incapacity for work
Depending on the severity of the lesion, they are 14-28 days. Possible disability in the event of complications, loss of vision.
Further management
Observation of an ophthalmologist at the place of residence for several months (up to 1 year). Control of ophthalmotonus, state of ST, retina. With a persistent increase in IOP and the absence of compensation on a medical regimen, antiglaucomatous surgery is possible. With the development of traumatic cataract, removal of the cloudy lens is indicated.
FORECAST
Depends on the severity of the burn chemical nature the damaging substance, the timing of the patient's admission to the hospital, the correctness of prescribing drug therapy.
