Many people consider ptosis to be a non-serious disease: it is not life-threatening, does not cause serious complications and is, rather, a cosmetic defect. However, drooping eyelids can cause various psychological problems, and in advanced cases, lead to severe deterioration and even loss of vision.
Description and classification of ptosis
Ptosis is a drooping of the eyelid
Some parts of the human body can change their location - go down. If in the case of kidneys or breasts this happens almost imperceptibly, then drooping eyelids are visible to the naked eye. This disease is called ptosis, which means “fall” in Greek.
The problem can occur in both adults and children, including infants. This defect is most often passed on to children from their parents, being hereditary. In adult men and women, ptosis occurs due to various reasons: due to muscle paralysis, tumors, scars.
In older people, ptosis most often develops due to decreased skin elasticity and age-related changes. In youth, the border between the eyelid and cheek is invisible, but over time, the subcutaneous fat covering the bone of the orbit moves down, forming characteristic “bags” - ptosis of the lower eyelid appears. The tissues above the eyes also undergo changes. Excess skin forms on the upper eyelid, which moves downward, covering the iris. Age-related ptosis can be divided into 4 stages.
- Ptosis only on lower eyelids.
- Drooping of both lower and upper eyelids.
- Along with the eyelids, the tissues of the cheeks and cheekbones droop, and deep nasolabial folds form.
- Drooping of the corners of the eyes, exposure of the sclera, formation of a deep nasolacrimal groove.
 Ptosis can develop not only in an adult, but also in a child
Ptosis can develop not only in an adult, but also in a child
Ptosis causes significant discomfort for both older and younger people. Young people have a lot of complexes about their appearance, and old people, who often suffer from poor eyesight, have to strain a lot to see anything with a half-closed eye. Patients are often forced to tilt their heads back to increase the viewing angle, taking a characteristic “stargazer pose.”
Depending on the cause, ptosis can be congenital or acquired. If a pathology is detected in a newborn child, most often this indicates that one of his relatives already has this disease. In addition, ptosis in infants may be associated with improper formation of the eyes or underdevelopment of certain muscle groups. In this case, the disease is accompanied by decreased vision and.
Acquired ptosis has the following types:
- neurogenic - occurs due to neurological problems;
- mechanical - provoked by shortening of the eyelid due to the appearance of a scar or tumor on it;
- myogenic - is a complication of myasthenia gravis, which is characterized by disturbances in the functioning of striated muscles;
- aponeurotic - appears due to the separation of the tendon that lifts the eyelid from its attachment site due to injury or age-related changes;
- false - provoked by excess skin on the eyelid.
Eyelid ptosis can be either unilateral or bilateral. In the first case, only one eye is affected, and in the second, the disease progresses in both organs of vision at once. As a rule, unilateral ptosis is often acquired, while bilateral ptosis is a congenital pathology.
Elena Malysheva about ptosis - video
Causes and symptoms
Congenital and acquired forms of the disease appear under the influence of completely different reasons.
Congenital ptosis occurs due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- underdeveloped levator muscle upper eyelid;
- pathologies of the oculomotor nerve;
- Hun's syndrome, which is manifested by drooping of the eyelid when the masticatory muscles work;
- blepharophimosis, i.e. too narrow palpebral fissure.
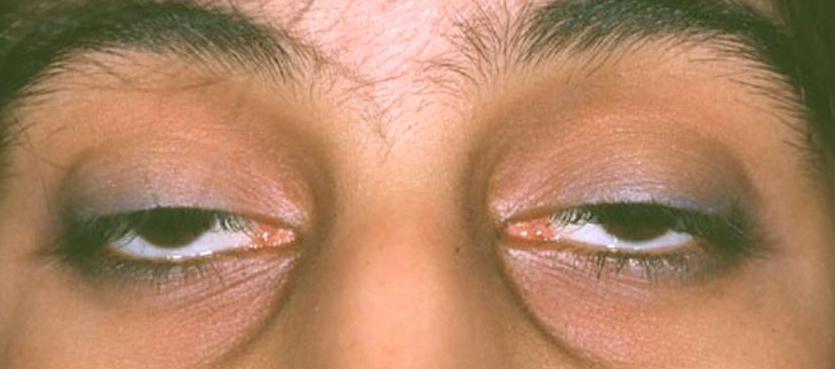 Bilateral ptosis is most often congenital
Bilateral ptosis is most often congenital
The causes of acquired ptosis may be the following factors:
- paralysis of the oculomotor nerve, which occurs with various tumors and diabetes;
- chronic kidney and cardiovascular diseases;
- rapid fatigue of the muscles that lift the eyelids;
- eye injuries;
- advanced age;
- scars in the eye area.
The last reason is a consequence of operations either cosmetic procedures. Thus, ptosis often occurs after Botox injections and other interventions for facial rejuvenation.
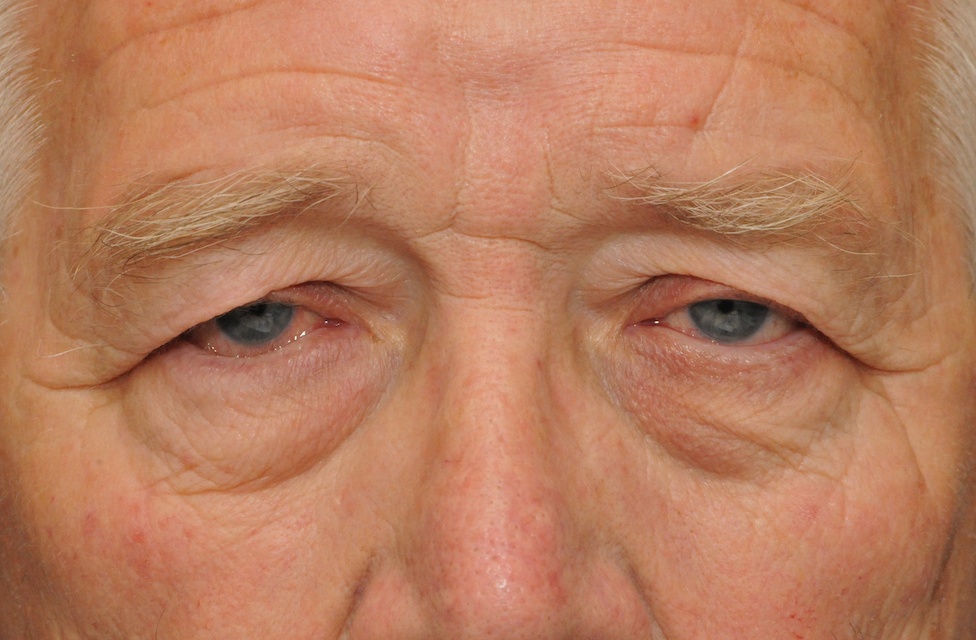 Age-related ptosis - common occurrence among the elderly
Age-related ptosis - common occurrence among the elderly
The main symptom of ptosis is drooping of the upper or lower eyelid. Many other symptoms may also indicate an anomaly:
- rapid fatigue of the visual organs;
- double vision;
- irritation, redness and dryness of the eyes, a feeling of heaviness;
- strabismus;
- inability to lower or raise the upper eyelid.
Ptosis also comes in varying degrees of severity. If untreated, the disease progresses quite quickly from partial to complete drooping of the eyelid.
Degrees of ptosis - table
When the first signs of drooping eyelid appear, do not hesitate to visit a doctor. Timely treatment can return the patient to his previous appearance without the use of surgical correction methods.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of ptosis are so vivid that the patient can make a diagnosis on his own. You need to see a doctor so that a specialist can determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
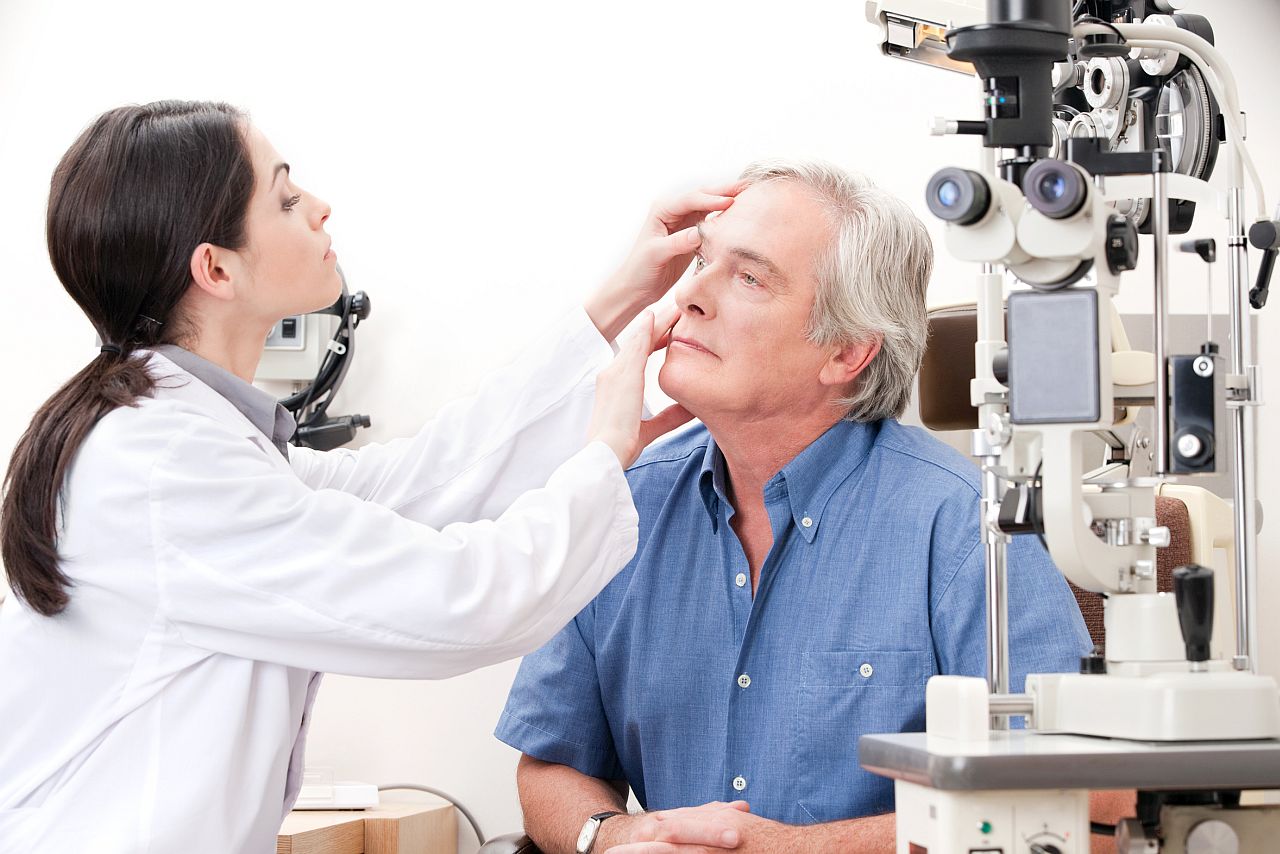 During the examination, the doctor finds out the cause of ptosis and, depending on it, prescribes treatment.
During the examination, the doctor finds out the cause of ptosis and, depending on it, prescribes treatment.
Before the examination, a conversation is held with the patient, on the basis of which the doctor makes a conclusion about whether the pathology is congenital. The course of treatment can also be affected by the presence of other diseases in a person, so the specialist’s responsibilities also include drawing up a complete picture of the patient’s health, because this defect is rarely an isolated pathology. For example, if we are talking about acquired myogenic ptosis, the patient must have myasthenia gravis - chronic muscle weakness, which the patient simply cannot be unaware of.
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor examines the patient, which includes:
- measurement of visual acuity and strabismus angle;
- determination of intraocular pressure;
- visual examination to determine weakness of the muscle responsible for raising the eyelid;
- height measurement upper eyelid;
- establishing muscle tone;
- observation of the symmetry of eyelid movements during blinking.
If the doctor determines that ptosis is caused by oculomotor nerve palsy, he may order an ultrasound of the eyes, X-rays of the orbit, and magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of the brain. These studies make it possible to identify neurological disorders and develop a treatment plan taking into account the identified pathologies.
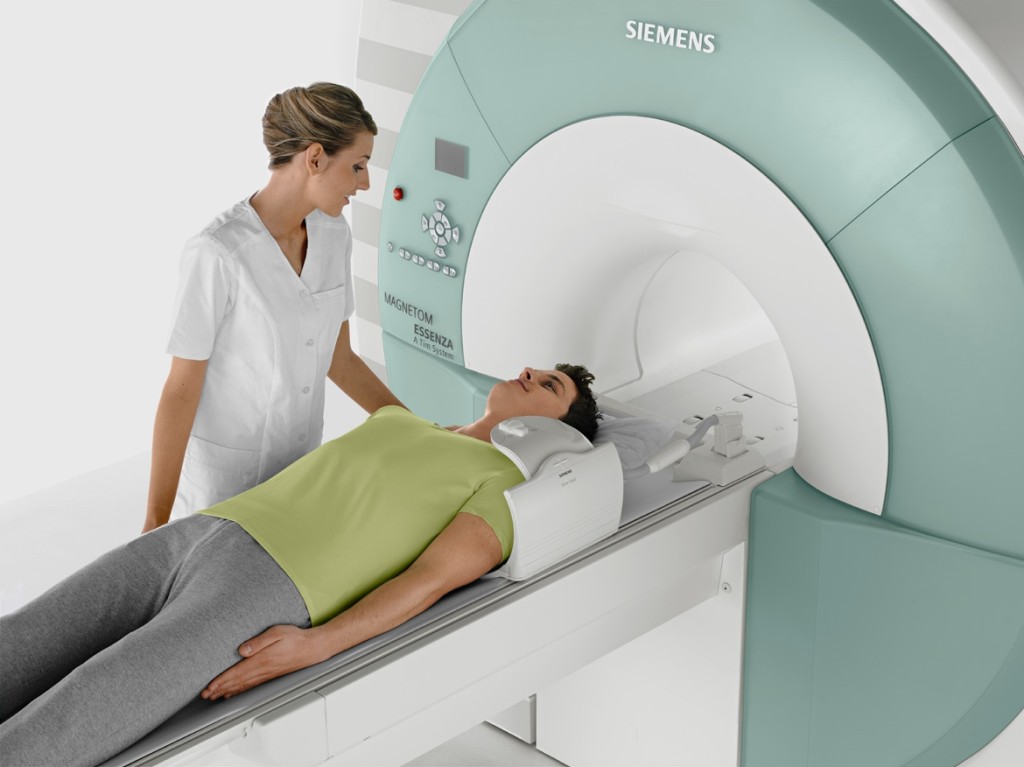 MRI of the brain allows us to find out the cause of ptosis
MRI of the brain allows us to find out the cause of ptosis
Treatment
Most often, drooping eyelids are corrected surgically, but in some cases conservative treatment is also effective. As a rule, the doctor prescribes it if the cause is age-related changes or in cases where the patient is diagnosed with an acquired neurogenic type of disease.
Conservative
Non-surgical treatment of ptosis is a rather lengthy process, and it can be achieved with its help. positive result It’s not always possible. Therefore, doctors prescribe such procedures only if they have firm confidence in their effectiveness for a particular patient.
Conservative treatment consists of using the following methods.
- Use of tightening agents. Creams and ointments with a lifting effect are prescribed in cases where the cause of ptosis is the advanced age of the patient. Such remedies only help in cases of partial ptosis. If the eyelid covers more than half of the pupil, they will not give a pronounced effect. The tightening cream should be used daily, without skipping, and the drug should be tested before starting treatment, since people prone to allergies may experience undesirable reactions to such products.
- Massage. Regular massotherapy helps strengthen the muscles of the eyelids, but it is most often useless with pronounced ptosis.
- Fixing the eyelid with adhesive tape. This measure is also aimed at strengthening the muscles of the upper eyelid and is effective only on initial stages diseases. Doctors rarely prescribe similar procedure, since it causes additional discomfort to patients, both physical and psychological.
- UHF therapy. Treatment with a high-frequency electromagnetic field is very effective for neurogenic ptosis, when it is necessary to restore nerve function.
- Galvanization. Local application of low-intensity current also makes it possible to achieve improvements in the treatment of neurogenic ptosis, but is ineffective in the case of other types of this disease.
- Paraffin therapy. Paraffin masks are used to tighten the facial muscles and are effective at the stage when ptosis is not yet pronounced, but the pathological process has already begun. They are used 1–2 times a week until the desired effect is obtained and 2–3 times a month for preventive purposes.
- Exercises for the eyes. With the help of myogymnastics you can tighten and strengthen your facial muscles. For this, various exercises are used: opening and closing the eyes, circular rotations, bringing the eyebrows together while fixing them with your hands. Such gymnastics is very effective in quality preventative measure, however, significant improvements with its help are extremely rarely achieved.
- Taking medications. If ptosis is a complication chronic diseases, including neurological ones, treatment comes down to eliminating the cause of the disease. In this case, a neurologist or other specialist, along with physiotherapy, may recommend taking appropriate medicines. Ptosis will disappear on its own after the disease that caused it is eliminated.
If conservative methods are ineffective, ptosis is eliminated through surgery.
 The use of products with a lifting effect can prevent drooping eyelids
The use of products with a lifting effect can prevent drooping eyelids
Surgical methods of correction
In most cases, surgery is used to treat ptosis. Surgical treatment is justified in the following cases:
- when treating children (over three years old);
- to eliminate congenital drooping of the eyelid;
- in advanced cases, when the eyelid covers more than half of the pupil;
- to get the fastest possible results.
In the case of blepharoplasty, the eyelids acquire a normal appearance immediately after the operation, and the effect lasts for a long time. Timely surgical intervention is especially important if a child suffers from ptosis. In babies, their visual organs are just developing, and drooping eyelids can have an impact on them. negative impact, causing strabismus and other problems. Therefore, for children who are already 3 years old, ptosis is most often eliminated surgically, without resorting to conservative treatment.
There are several types of surgeries to correct drooping eyelids.
- Stitching to the frontal muscle is carried out when there is insufficient mobility of the upper eyelid.
- Muscle resection is performed with moderate eyelid mobility and shortening of the muscle that prevents it from drooping. The surgeon makes an incision in the eyelid, removes a small area of skin and cuts off part of the muscle.
- Duplication of the muscle aponeurosis is carried out with good mobility of the upper eyelid. To lift it, you need to shorten the muscle that controls the eyelid.
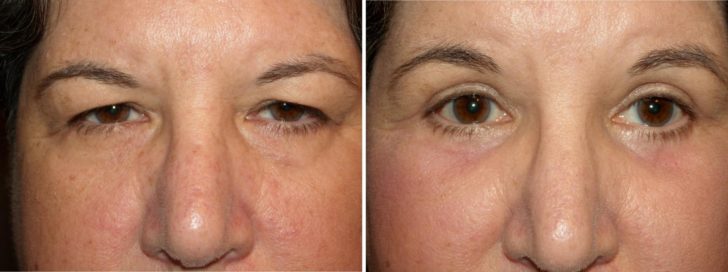 Surgery can literally transform a person's appearance
Surgery can literally transform a person's appearance
As a rule, operations are performed under local anesthesia, sutures are removed within 3–5 days, and rehabilitation period does not cause significant inconvenience to patients. With proper intervention, relapses of ptosis rarely develop, and the person can return to to the usual way life. The choice of a clinic and a specialist who will perform the operation should be approached very carefully, because unprofessional actions of a doctor can provoke a number of complications: lacrimation, eyelid inversion, sloppy scars, etc.
Feedback on the operation performed
I am 16 years old, I have congenital ptosis, I had 5 operations at the Fedorov clinic in Novosibirsk (I live in Magadan). I remember the first 4 operations vaguely, because it was very small, but thanks to them, my ptosis is not very noticeable. I can open my eyes wide, but at the same time I don’t open them with the eyelid muscle (it doesn’t work), but I don’t even know how to explain it... With the eyebrow muscles or something. With makeup, ptosis is even less noticeable. I'm suffering. It’s still a complex, but what a complex it is. I can’t come to terms with the fact that I’ve been like this my whole life...
Morgan le Fay
My son is also 3 years old, in July we had surgery on him in Ufa, at the All-Russian Eye and Eye Center plastic surgery. We had ptosis, one eye - 2, the second - 3 degrees, after the operation the eyes became wider, more open and there was no forced position of the head up.
Hope
http://www.woman.ru/beauty/plastic/thread/4045387/
My son has congenital ptosis of both eyes, grade 4. Surgical treatment passed at the age of 2 years, and underwent resection of the levator. The operation lasted about 2 hours under general anesthesia. The result was not impressive: the right eye was opened halfway, the left - a little less. But we have serious neurology, now the child is almost 6 years old, and I can say that the more he develops, the better his eyes open, i.e. there is an obvious connection between the general improvement in the child’s neurological status and the opening of his eyes. It is likely that overall nerve conduction improves, hence the wider eyes.
http://eka-mama.ru/forum/part56/topic271358/
Folk remedies
Treatment with herbs and others traditional methods does not bring a noticeable effect on drooping eyelids and is justified only as preventive procedures or as additional remedy in parallel with traditional therapy.
The following recipes help tighten and strengthen the skin of the eyelids at home:
- Grated raw potatoes. Grate the potatoes on a fine grater, place in the refrigerator for 30 minutes, and then apply the mixture to clean eyelids. Leave the mask on for 15 minutes, then rinse it off with warm water.
- Chamomile and thyme. Pour 2 tablespoons of chamomile or thyme herb with a glass of boiling water and cook in a water bath for 15–20 minutes. After the broth has cooled, you need to wipe your eyelids and face.
- Rosemary and lavender. Pour 1 tablespoon of lavender and rosemary into a thermos, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 3-4 hours. Wipe your eyelids with the cooled infusion 3 times a day.
- Ice cubes. To increase skin elasticity, it is useful to wipe your face with ice cubes - you can freeze cucumber juice, a decoction of birch leaves or chamomile infusion.
- Sesame oil and egg yolk. Beat the yolk of 1 egg, add half a teaspoon of sesame oil, mix well and apply the mixture to your eyelids. After 20–30 minutes, rinse off the mask with warm water.
Regular use of folk remedies can delay age-related ptosis for some time.
Folk remedies for the prevention of ptosis in the photo
 Potatoes contain starch, which has positive influence on loose skin
Potatoes contain starch, which has positive influence on loose skin
 Chamomile is a recognized antiseptic
Chamomile is a recognized antiseptic  Thyme is used to treat many diseases, as well as to prevent ptosis.
Thyme is used to treat many diseases, as well as to prevent ptosis.  Rosemary tightens the skin of the eyelids
Rosemary tightens the skin of the eyelids  Lavender is both a cosmetic and medicinal raw material.
Lavender is both a cosmetic and medicinal raw material.  Ice cubes cool the skin, making it firmer
Ice cubes cool the skin, making it firmer  Yolk and sesame oil - base nourishing mask for eyelids
Yolk and sesame oil - base nourishing mask for eyelids
Prognosis and possible complications
Ptosis of the eyelid can be successfully treated surgically, but conservative methods may not bring desired results. In this case, you should not postpone surgical intervention, since drooping eyelids can provoke ailments such as strabismus and amblyopia, which leads to significant deterioration of vision.
Sometimes the operation does not bring results. If after the intervention a person experiences persistent complete ptosis of one or both eyes, this is grounds for disability.
The operation does not always go smoothly. Most often, after the intervention, patients experience the following complications:
- sore eyelids;
- loss of sensation;
- dryness and pain in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- slight asymmetry of the eyelids
- swelling and inflammation of the skin around the eyes;
- inability to completely lower the eyelids.
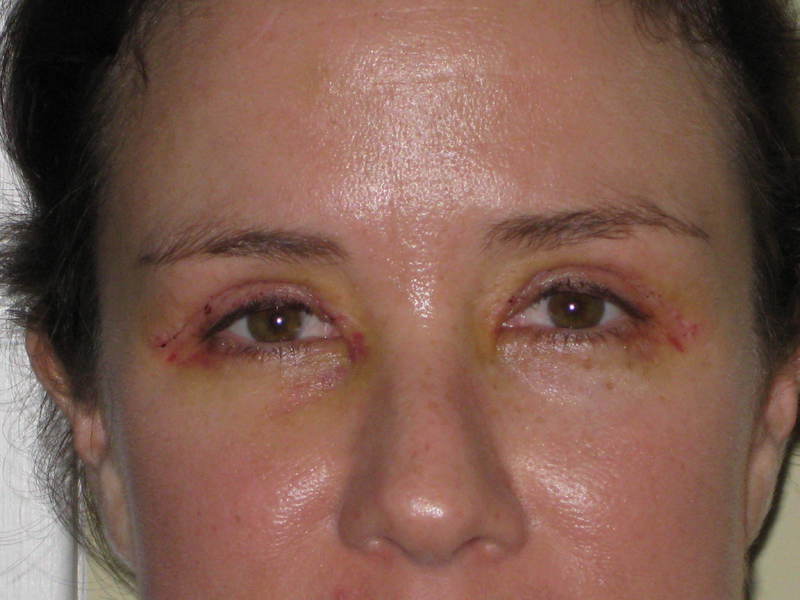 Edema and others unpleasant phenomena after surgery they usually disappear within a week
Edema and others unpleasant phenomena after surgery they usually disappear within a week
As a rule, most complications resolve within 1–2 weeks. If symptoms continue to bother you, the patient needs further examination and treatment.
Prevention
The following measures help prevent the appearance of ptosis:
- Timely treatment of diseases that lead to drooping eyelids (in particular, eliminating problems with the facial nerve).
- Myogymnastics for the eyes and facial muscles.
- Facial massage, including self-massage.
- Usage folk recipes for tightening the skin of the eyelids.
- Regular use of masks, creams and serums with a lifting effect to prevent age-related changes.
When the first signs of ptosis appear, consult a doctor immediately. In the early stages, drooping eyelids can be treated without surgery.
Exercises to prevent drooping eyelids - video
Ptosis of the eyelid causes people a lot of inconvenience, both physical and psychological. In some cases, this problem can be eliminated using conservative methods, but more often the matter ends with surgery, especially in the congenital form of the disease. Don't be afraid surgical intervention: provided you choose the right specialist, the operation will return you to an attractive appearance, A possible complications will be kept to a minimum.
PTOSIS of the upper eyelid is a fairly common symptom, characterized by drooping of one or two upper eyelids due to decreased muscle tone or impaired nerve patency.
PTOZ of the eyelid as an independent disease does not pose a significant health hazard, but is a significant aesthetic drawback and often creates significant problems with vision. With severe disruption of innervation, patients often have to raise their chin and eyebrows high to open the pupil and see objects.
Now let’s talk in more detail about what PTOZ of the upper eyelid is, what its causes are and whether correction is possible.
Causes and etiology
There are both congenital and acquired types of the disease. Specialists definitely recognize bilateral PTOZ as congenital, when there is drooping of the upper eyelid in both the left and right eyes.
Congenital and acquired types of the disease are possible. No more than 25% of people suffering from the disease are characterized by congenital drooping of the upper eyelid. The causes are predominantly genetic. Less commonly, PTOD is a consequence birth trauma. Quite often, the congenital type of the disease is associated with other visual anomalies: strabismus and amblyopia.
If PTOS does not accompany other eye diseases and is caused only by underdevelopment of the upper eyelid muscle, then it is dominant in inheritance. As a rule, if one of the parents has PTOSIS, the defect is passed on to the child as a dominant trait.
Less common are cases in which drooping of the upper eyelid is caused by pathologies optic nerve. A patient with this picture of the disease is characterized by the so-called “stargazer pose” - a constantly raised chin or raised eyebrows.
Sometimes congenital PTOS of the upper eyelid is associated with a rare genetic disorder known as palpebromandibular syndrome. With it, the muscles of the upper eyelid are innervated by the action of the jaw muscles, in other words, the eyelid opens completely when a person chews. Most often, the disease is associated with strabismus and underdevelopment of one of the eyes.
Another rare genetic disorder that causes drooping eyelids is blepharophimosis.
This disease is characterized by underdevelopment of the palpebral fissure - it is abnormally short and does not allow either lowering or raising the eyelids. In this case, the presence of double blepharoptosis is noted - both eyelids are closed by more than 2.3 mm, which creates significant difficulties for vision. With blepharophimosis, inversion of the lower eyelids may occur.
The manifestations of congenital PTOSIS can, as a rule, be stopped or minimized only by surgery.
Acquired PTOZ of the upper eyelid is much more common. The causes of the disease can be due to both serious neurogenic disorders and simple mechanical obstacles when opening the eyelids.
Neurogenic PTOS is characterized by the presence of diabetic brain pathologies and tumors that compress the oculomotor nerve. The eyelids may close completely. For PTOSIS of the upper eyelid caused by pinching of the oculomotor nerve, treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease. In some cases (for example, when treating corneal lesions), specialists artificially cause complete drooping or significant drooping of the upper eyelid by surgically compressing the oculomotor nerve.
If significant damage to the tendons has occurred in the tissues of the upper eyelid, the muscles of the upper eyelid lose tone - this picture of the disease is characteristic of aponeurotic PTOSIS. As a rule, drooping eyelids due to tendon damage occur as a result of injuries and after the entry of foreign objects.
Almost always acquired PTOS accompanies myasthenia gravis, a disease in which the fibers of the body muscles, including the oculomotor muscles, lose tone due to the presence of antibodies in the muscle tissue of the eyelid. With myogenic PTOSIS, the eyelids of both the left and right eyes droop. When diagnosing the disease, endorphin is used; after its administration, symptoms (including bilateral PTOS) disappear for a while.
Often atony of the eyelid muscles is a consequence of diseases nervous system, including stroke and meningitis.
Neurogenic PTOS also causes Horner's syndrome, a specific lesion of the sympathetic nervous system with cervical nerve palsy. When treating PTOSIS of a neurogenic nature, efforts are aimed at general recovery - experts do not recommend performing cosmetic surgery while fighting the consequences of the underlying disease.
Mechanical drooping of the eyelids is characteristic of tumors that foreign body and tissue scarring due to injury.
Diagnosis of PTOS
When the upper eyelid droops, a specialist must clearly understand the etiology of the disease; diagnosis comes down to finding the causes. If there is drooping of the upper eyelid, the reasons may be different. In case of congenital PTOSIS, treatment tactics come down to minimizing and relieving symptoms; in case of acquired PTOSIS, it is to eliminate the primary causes.
First of all, the specialist conducts a differential diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude infectious diseases and paresis.
Next is a detailed survey and anamnesis collection. The specialist receives information about cases of the disease in the family, as well as the presence (or absence) of third-party pathologies that can cause or provoke drooping eyelids. If PTOS of the upper eyelid is noted, only a doctor can determine the cause.
During diagnosis, an ophthalmological examination is required to identify possible violations, check visual acuity and degree of intraocular pressure.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND! To quickly and safely restore vision, our readers recommend the drug Sokolit. This miracle drug has been on the European market for 2 years; its effectiveness is several times higher than laser correction vision and such drugs as Blueberry Forte. It is aimed at eliminating the causes, not the symptoms, of poor vision, its effectiveness and safety have been proven in clinical studies.
In cases of acquired disease, a specialist often refers the patient to CT and MRI; sometimes PTOZ serves as the primary symptom of tumor diseases of the brain.
Treatment methods
Treatment of PTOS of the upper eyelid is carried out both conservatively and surgically. Only a doctor can tell you what to do in a particular case. Many people try to carry out treatment at home without diagnosis and supervision from a specialist.
Conservative method - treatment without surgery. This method is used to restore lost muscle tone and nerve conduction. How to treat such a disease? The range of activities includes:
- Physiotherapy.
- Muscle and nerve stimulation (using galvanic current)
- Application of a special patch for mechanical lifting of the eyelid. Significantly aggravates cosmetic imperfections, but necessary to avoid further complications, especially for children.
- Laser therapy.
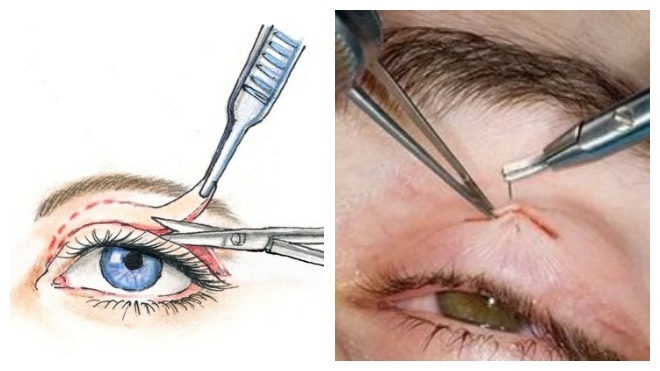
According to experts, conservative treatment measures are rarely successful, but are quite effective in treating PTOSIS of neurogenic etiology, when the disease is caused by pinching of the oculomotor nerve. For blepharophimosis and scars on the tissue of the upper eyelid, only surgical intervention is indicated; in other cases, eyelid surgery is prescribed after 6 months of conservative treatment, which has proven ineffective.
Correction of PTOSIS of the upper eyelid almost always involves surgical intervention.
A particularly operative method of treatment is indicated for children long absence adequate treatment as you get older can turn cosmetic defect into a progressive disease.
Tactician surgical treatment some. If the upper eyelid has drooped and almost lost its mobility, the surgeon tries to cure and lift it by suturing it from above (to the forehead muscle). This method of treatment is not very effective, but is practically free of complications. This surgery is sometimes performed on children (when the eyelid droops) as an intermediate step to reduce the risk of vision loss.
In the case where the drooping eyelids are mobile, the surgeon resorts to resection of the muscle. Through a small incision, the doctor removes a small area of skin and cuts the muscle that lifts it. Reducing the volume of muscle tissue does not allow the eyelid to droop spontaneously.
In most cases post-operative recovery It goes away quite quickly and without complications - the sutures are removed already 3–5 days after the operation.
The prognosis is generally favorable, repeated interventions after blepharoplasty are almost never performed, and the effect lasts for life.
Home and traditional methods
Many people decide to treat PTOZ at home without supervision from an ophthalmologist. The disease has been known for a long time, so treatment folk remedies- a very common phenomenon.
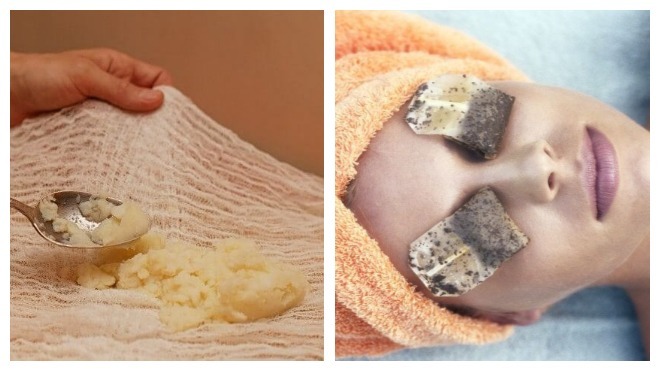
In order to increase the therapeutic effect during treatment at home, several methods are usually used at once.
Common and inexpensive remedy- lifting mask based on natural ingredients:
- Egg yolk mixed with sesame and olive oils, applied to the skin of the eyelid for 20 minutes.
- Finely grated and cooled potatoes are applied for 15–20 minutes. According to practitioners, the colder it is, the more effective it is.
- Grated thyme and chamomile are applied to the eye for 15–20 minutes. Indeed, the natural antiseptic in chamomile can eliminate inflammation that often occurs during the use of other folk remedies.
The use of masks is possible and gives a certain therapeutic effect, but in the case of PTOSIS of neurogenic or genetic etiology, such methods will be powerless, since they do not eliminate the root cause of the disease.
Therapeutic gymnastics and massage
More effective method. It can have a positive effect even with a congenital type of disease, if it is associated with low muscle tone. To achieve the effect, you need to do gymnastics regularly for quite a long time.
- They start with a warm-up: you need to open your eyes as wide as possible, in a circular motion look around you and squint. Repeat 5-6 times.
- Keep your eyes open as much as possible for 10 seconds. Close your eyes tightly for 10 seconds. Repeat 5-6 times
- As a second exercise, bring the eyebrows to the bridge of the nose with your index fingers and repeat until the muscles hurt.
- Final exercise - index finger stroke the eyebrow, gradually accelerating and pressing harder
The effectiveness of eye gymnastics is due to an increase in the general tone of the oculomotor muscles, and as a result, the muscles of the drooping eyelid.

In combination with regular diagnostics, moderate therapeutic effect has a massage, increasing the tone of the eyelid muscles and improving their blood supply.
The procedure is carried out in 4 stages:
- Preparatory. You need to thoroughly wash your hands and the skin around your eyes. Before starting the massage, make sure there is no irritation or redness. Before starting, apply clean skin moisturizing cream
- Elementary. The skin around the eyes is stroked with the index fingers; they pass along the eyebrow without touching the eyelid. After you make a few circles, you need to blink a little
- The main one is to rub the eyebrows one by one with the index finger in one direction from the bridge of the nose. Repeat 10-15 times for each eyebrow.
- Repeat First stage as a final one.
In home therapy, ice cubes made from water or chamomile decoction are used to relieve swelling. Applying ice before or immediately after a massage is not recommended, as this reduces the effectiveness of the procedures.
Conclusion
Even if self-treatment had a therapeutic effect, professional diagnosis, consultation and monitoring by an ophthalmologist are necessary to avoid complications.
Plan your surgery carefully, especially if the surgery involves muscle resection. Incorrect truncation can lead to the eyelid not closing at all - before the operation, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the reputation of both the clinic and the specific specialist. Do not save on time and money - a correctly performed operation will forever eliminate the need for repeated surgical interventions.
If you look directly at a person’s face, you can see that the upper eyelid of the right eye is asymmetrical in relation to the left. When people's skin hangs by at least 0.2 centimeters, then, regardless of age, they look tired and sad. Increased fatigue occurs due to the fact that a person puts a lot of effort into just blinking.
What is eyelid ptosis
Abnormally low position eyelids are called ptosis. The disease can be congenital or acquired and differs in the duration of the course or the age of the patient. Ptosis can be complete or incomplete, unilateral or bilateral. According to the severity of the pathology, the pathology is classified when the edge of the upper eyelid:
- covers a third of the pupil – this is degree 1;
- closes 2/3 of the pupil – 2nd degree;
- completely covers the entire pupil – 3rd degree.
Patients complain of eye fatigue and poor vision. It is very difficult for them to blink, so they are forced to constantly tense the muscles of their eyebrows and forehead. The eye does not close completely, as a result of which the mucous membrane is irritated. If ptosis is advanced, the patient develops amblyopia (visual impairment), double vision or strabismus. Children often tilt their head back to raise the upper eyelid.
Why does drooping eyelid occur?
The disease develops due to damage to any nerve. When all the muscles of the eye are fully functioning, the nerve impulse starts from the central nervous system and travels along the oculomotor canal to the eye muscle. If it is interrupted at some stage, the eyelid droops. Pseudoptosis (false) occurs for another reason. In this case, the palpebral fissure is narrowed due to a nervous tic or hysteria.
Congenital
If the eye muscle is poorly developed or absent due to a hereditary reason, then this is congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid. Sometimes a baby is born with such a defect after a neurological disorder in which the lateral nuclei of the oculomotor nerve are underdeveloped. May play a role genetic disease The child has. If the congenital pathology is not treated on time, then in the future it will lead to the development of anisometropia, when the difference in the vision of the two eyes is up to 3 diopters or other eye diseases.
Acquired
There are many reasons for acquired eyelid drooping. The disease can result from injury or inflammation of the optic nerves, which causes paralysis (partial or complete). Upper eyelid ptosis may develop after Botox when the ligaments are weakened. Although the eye muscles remain connected to the bones, they become stretched and the skin sags. Sometimes the disease is acquired with age during the development of chronic diseases of the kidneys, heart, diabetes mellitus, Horner's syndrome.
Diagnosis and treatment
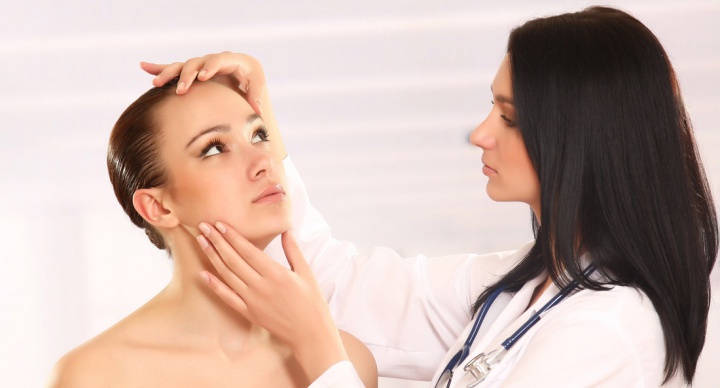
All of the above symptoms of the disease are visible to the naked eye. Ophthalmologists can only find out the causes of the pathology, make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. During the examination, the doctor takes into account the difference in the course of the disease, which consists in damage to different areas of the visual analyzer. If the pathology is congenital, then the levator muscles of the eyelids are nonfunctional.
The acquired variant is characterized by a muscular aponeurosis responsible for lifting. An important point When diagnosing, it is necessary to clarify with the patient whether a similar pathology occurred in the parents. The method of treatment depends on the answer, because for the acquired variant a completely different therapy is provided, since the disease is caused by an elastic and elastic muscle, in contrast to a congenital disease.
Treatment for a stretched eyelid must begin immediately to avoid complications, because the disease does not go away on its own. Today, surgery, which is indicated from 3 years of age, is considered a successful solution to the problem. If the child has not reached the mentioned age, then for the purpose of prevention, the baby’s upper eyelid is tightened using a plaster.
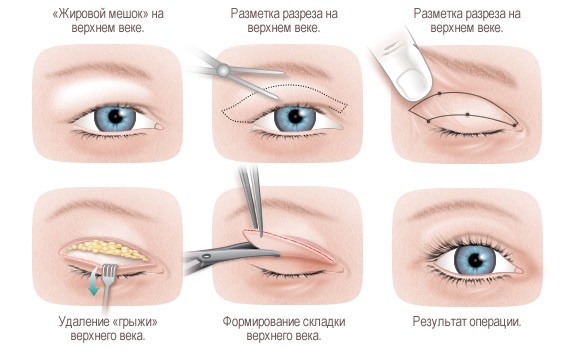
Surgical correction of ptosis of the upper eyelid
An ophthalmologist performs surgical correction of the eyelid using local anesthesia. General anesthesia is given to children. The operation lasts on average 1.5 hours. If the cause of the disease is any chronic pathology, then surgical intervention is prescribed only after it has been eliminated. How the operation is performed:
- a small strip of skin is removed from the upper eyelid;
- the orbital septum is cut;
- the incision divides the aponeurosis, which is responsible for raising the eyelid;
- the stretched part of the aponeurosis is excised;
- the rest is sutured to the lower cartilage of the eyelid;
- superimposed continuous cosmetic stitch;
- a sterile bandage is applied.
Exercises for upper eyelid ptosis
At home, you can try to remove congenital or acquired ptosis using therapeutic exercises. Treatment takes a long time, but if done regularly, there is an option to avoid surgery. Exercises for the facial muscles (repeat each from 6 to 10 times):
- Warm up. Open your eyes wide, look around in a circular motion, then close your eyes sharply.
- Open your eyes as much as possible. Hold your gaze without blinking for 10 seconds, then close it tightly, tensing your muscles tightly. Hold for another 10 seconds, then relax.
- Place your index fingers on your eyebrows and press down. Try to bring your eyebrows together until the muscles ache.
- Massage the eyebrow above the ptosis with your index finger. Start with stroking, gradually increasing the pressure and tempo.
Treatment of ptosis without surgery
The disease is also treated with therapeutic methods. If ptosis of the eyelid is 1st degree, then a positive result can be given local treatment. If the pathological process is caused by aging, firming creams and physiotherapeutic procedures can be used: paraffin therapy, UHF, galvanization. If there is no effect on the patient even on early stage drooping eyelids may be referred for surgery.
Video: causes and elimination of ptosis of the upper eyelid
If your eyelids droop over your eyes, the reasons can be very different. But the result is unchanged: a tired, gloomy appearance. Let's talk about why the upper eyelids droop and how you can deal with this problem.
Eyes with drooping eyelids are not a death sentence
First of all, it should be said about those who inherited drooping eyelids from their parents. Most likely, one of your ancestors belonged to the Mongoloid race, so this structure of the century is genetic. If this is so, there is no need to be complex, because this is your distinctive feature, characteristic feature appearance that can be played to advantage. Watch video tutorials from Korean and Japanese girls showing different kinds makeup for eyes with drooping eyelids. They will help you look attractive and fresh, teach you to remove the feeling of a gloomy look and “open” your eyes. If you have a drooping eyelid on one eye, or the problem has appeared relatively recently, it makes sense to try to get rid of it. But to do this, you need to find out why your eyelids droop.
What causes the upper eyelids to droop over the eyes?
There are quite a few reasons why you have drooping eyelids. First of all, these are the following factors:
- age-related skin changes;
- overweight;
- kidney problems;
- disturbed water-salt balance in the body;
- incorrect sleeping position;
- bad pillow;
- allergic reaction and incorrectly selected facial skin care products.
Let's talk in more detail about each of these reasons.
When it comes to age-related changes, everything is quite clear: the muscles of the eyeball and eyebrows have lost their tone, the skin has become more flabby, wrinkles have appeared and, as a result, a drooping eyelid. At this stage, only blepharoplasty will help and high-quality cosmetics with a lifting effect.
If you are overweight, the cause of drooping eyelids may be fatty hernias. They can also be eliminated solely by surgery.
If you have suddenly lost weight and as a result have developed the first wrinkles, you can cope with drooping eyelids by using a cream with a tightening effect and doing special exercises for eyes. The main thing in this case is regularity.
The cause of drooping eyelids may be kidney problems. Have you noticed that your face swells in the morning, and by the evening your eyelid becomes smaller? This is a reason to contact a neurologist and urologist.
Indirectly, disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system cause disturbances in the water-salt balance in the body, which can also cause swelling in the upper and lower eyelids. Try drinking more clean water and do not eat salt or foods high in salt. Positive effect usually manifests itself after a few days of such a diet. Chamomile compresses also help relieve swelling.
If you like to sleep on your stomach, or use too large a pillow while sleeping soft skin the eyelid can become deformed, and the rush of blood to the face can cause swelling. Change your sleeping position, buy an orthopedic pillow. This will help you look fresh!

Often the cause of drooping eyelids is allergies or improper facial care products. Try giving up makeup completely for a few days. If the drooping eyelid has become smaller, it means that you are allergic to one of the products you use.
Girls love to buy cosmetics, but do not always know how to apply them correctly. You bought good cream for eyelids with lifting, but it made your eyes swell much more, and the drooping eyelid only got worse? Most likely, you are using the product incorrectly. Remember: you need to apply it along the edge of the eye socket of the skull, retreating 2-3 centimeters from the eye itself. If you do not follow this rule, swelling of the eyelids will appear.
Ptosis of the eyelid is a fairly common pathology, which can be provoked by whole line reasons. Therefore, the seriousness of this problem should not be underestimated. Moreover, ptosis occurs in both adults and children.
At first glance, drooping eyelid seems to be an insignificant pathology; all the harm, which consists of slight interference with normal vision, is primarily cosmetic. However, even slight interference with vision can become a serious problem, because a person constantly strains his eyebrows in order to raise his eyelid. In serious cases, the patient even has to throw back his head in order to see objects better, and this head position, specific to ptosis, is called the “stargazer pose.”
Causes of ptosis
The causes of ptosis are numerous. Depending on the cause, eyelid ptosis may relate to one or another type of disease.
Types of ptosis and their characteristics depending on the cause
Drooping eyelids are classified according to several criteria. Thus, unilateral and bilateral ptosis are distinguished. In this case, bilateral ptosis is most often congenital, and unilateral, as a rule, is an acquired pathology.
1. Congenital ptosis
The above pathology is caused by an autosomal dominant type of genetic inheritance. This means that if one of the parents had congenital ptosis, there is a high probability of developing this pathology in the child. The cause of such ptosis, as a rule, lies in the underdevelopment of the muscle that raises the upper eyelid.
Sometimes the cause of congenital ptosis is a pathology of the nucleus of the oculomotor nerve, which is responsible for correct position century. Occasionally, ptosis causes weakness of the superior rectus muscle of the organ of vision, but more often it is developed normally. The previously mentioned “stargazer pose” is typical for a child, and when looking down, a higher location of the affected eyelid is revealed in relation to the healthy one.
Palpebromandibular syndrome. This pathology is very rare. It is characterized by synkinetic retraction of the ptotic eyelid upon stimulation of the pterygoid muscle. In other words, when the masticatory muscles work, the drooping eyelid rises. This is explained by the following: the development of nerve structures gives the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid, innervation from the trigeminal nerve, which innervates the masticatory muscles. The occurrence of an impulse and its passage along the trigeminal nerve stimulates the muscle - the levator of the eyelid. This syndrome is often accompanied by strabismus and amblyopia.
Blepharophimosis. A rather rare genetic pathology, which is characterized by an abnormally short palpebral fissure. With this pathology, bilateral ptosis is noted, while the muscles that raise the upper eyelid are underdeveloped. With blepharophimosis, inversion of the lower eyelids is also observed.
2. Acquired ptosis
This type of drooping eyelid is much more common than congenital, and is divided into several types depending on the cause of the pathology.
Neurogenic ptosis. A similar option occurs in the presence of oculomotor nerve palsy. Paralysis may develop due to diabetic neuropathy, tumors that compress it, or intracranial aneurysms. Internal ophthalmoplegia and pathology of the extraocular muscles are noted. Sometimes this ptosis is caused artificially in medicinal purposes, for example, with ulcers that do not heal due to lagophthalmos.
Myogenic ptosis. Develops with myasthenia gravis. As a rule, its bilateral variant is observed, the severity of which changes over time. Loads provoke drooping of the eyelid and cause. The effect of endorphin relieves the symptoms of ptosis for some time, which helps to correctly diagnose this pathology.
Aponeurotic ptosis. Often develops in older people due to the fact that the tendon of the muscle that raises the upper eyelid moves away from the plate to which it is attached. As a result, the tension and fixation of the eyelid disappears. Such ptosis can develop as a result of injury.
Mechanical ptosis. It appears due to horizontal shortening of the eyelid due to scarring or a tumor process.
Distinguish different degrees severity of drooping eyelid:
Partial (when the edge of the eyelid falls at the level of the upper third of the pupil);
Incomplete (when the eyelid is in the middle of the pupil);
Complete (when the eyelid covers the pupil).
Signs of ptosis
Of course, the main sign of ptosis is the drooping upper eyelid itself, but there are a number of symptoms that develop additionally with incorrect location century
Eye irritation.
Effort when trying to close your eyes.
Rapid eye fatigue due to constant efforts to ensure normal vision.
“Stargazer pose” is predominantly characteristic of children.
And double vision.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology comes down rather not to identifying drooping eyelids (it is noticeable anyway), but to finding out the reasons that caused it. The treatment tactics will be based on this. In this case the following is used:
A thorough interview will help you collect your medical history correctly. This is the key to successful diagnosis. The patient is asked whether cases of congenital drooping of the eyelid have been identified in close relatives, and it is found out whether he has diseases that can provoke the condition of ptosis.
A standard ophthalmological examination to determine intraocular pressure and identify possible visual field impairments.
Examination of the eye, which makes it possible to detect failure of the superior rectus muscle and epicanthus, which indicates congenital prolapse.
MRI and CT scan of the brain to diagnose the pathology that led to paralysis of the oculomotor nerve.
Treatment
Treatment of drooping eyelids is carried out conservatively and surgically.
Conservative treatment implies the use of drugs and agents that will affect ptosis of the upper or lower eyelid and reduce its effect. Unfortunately, it is not always effective and practically does not bring a positive result. That is why doctors practically do not recommend it.
Therapeutic treatment in the case of drooping eyelid, it is relatively rare, with the exception of neurogenic ptosis. In this case, treatment is aimed at restoring nerve function. UHF therapy is used locally, galvanotherapy, etc. If there is no effect, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Conservative methods also include temporary fixation of the affected eyelid with a plaster. True, this aggravates the cosmetic defect, and the patch itself creates additional inconvenience.
Surgery
In the vast majority of cases, ptosis can be treated surgically, so you should not postpone surgery for long, especially in children. After all, adults have mature posture and vision, and therefore are less susceptible to complications, unlike children with their growing bodies. Therefore, if you notice changes in the child’s body regarding the visual system, namely drooping of the eyelid, immediately seek advice and help from specialists.
When the eyelid is not mobile enough, it is fixed to the frontal muscle by suturing it. This method, unlike others, has less functional and cosmetic effect, but makes it possible to avoid complications.
In cases where the excursion of the eyelid is moderate, resection of the muscle that elevates the upper eyelid is possible. It is the shortened muscle that prevents the eyelid from drooping. During the operation, a thin incision is made, and then a small area of skin of the eyelid is removed, the muscle is isolated and resected.
When the eyelid is well mobile, it is possible to apply a duplication of the aponeurosis of the muscle that controls the eyelid, which allows it to be significantly shortened, providing the eyelid with a normal position.
Choosing a clinic for the treatment of eyelid ptosis is a very important question, because the result of treatment and prognosis largely depend on the completeness of the examination and the professionalism of the attending physician. When choosing a medical institution, it is important to take into account not only the cost of the operation, but also the level of specialists (an unsuccessful operation can lead not only to relapse of the disease, but also to the appearance of cosmetic defects) and the reputation of the clinic. Pay attention to the experience of your attending physician with such ailments as drooping lower or upper eyelids. After all, it is a competent professional who will be able to offer relevant ways to solve your problem and help avoid negative consequences.
