Doctors call blepharitis a group of eye diseases manifested by prolonged inflammation of the eyelids. In this case, the pathological process mainly affects the ciliary edges of the eyelids.
Blepharitis in children develops quite often, because the child’s immunity is not fully formed, i.e. protective functions do not work at full capacity. And if there is any chronic illness or some kind of sluggish infectious process, then this creates additional conditions, favoring the development of blepharitis.
Causes and symptoms of blepharitis in children
In addition, external unfavorable factors, allergic diseases, etc. can lead to this disease.
Symptoms of blepharitis in a child are expressed in complaints of itching in the area of the edges of the eyelids. This itching can be characterized as barely noticeable or quite severe. In this case, you can notice that the edges of the eyelids are unnaturally red.
As a manifestation, a burning sensation coupled with lacrimation and a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the eye may also be noted.
During the examination, the ophthalmologist detects the presence of hyperemia and thickening of the eyelids. If there is an infection with the scaly form of blepharitis, then on the edge of the eyelid where the eyelashes grow, you can notice small scales, the skin under which is thinned and red.


The ulcerative version of blepharitis in children, the photo of which can be seen above, is characterized by the formation of purulent crusts that are very difficult to remove (in this case, as a rule, eyelashes fall off along with the crusts). If you manage to remove the crust, you can notice an ulcer in its place, which in the vast majority of cases bleeds.
Forms of blepharitis of the eye in children (with photos)
In its manifestations, this form is similar to a simple or scaly version of the disease. As a result of the examination, enlarged eyelash bulbs are revealed. At the root of the latter it is also noted dark color and translucent cylindrical couplings.
So-called telangiectasia may develop. They are shaped like stars or meshes and represent an expansion of the skin capillaries of a persistent nature. The appearance of multiple papillomas and focal pigmentation between the eyelashes is also possible.
The peculiarity of this variant of the course is that it may well cause a decrease in the child’s vision. The disease develops over a long period of time and is difficult to treat. There is a possibility of relapses.
With the development of this form of the disease general health the child is unwell and, as a rule, all types of activity are reduced.
This type of disease is not quite similar to other described forms of this disease. Photos of the eyes of children with this type of blepharitis are located below:


In this case, small blisters appear on the eyelash edge or on the upper part of the eyelid, resulting from inflammation. sebaceous glands. After these bubbles burst, in their place you can see small pinpoint scars, although this does not happen in all cases (the bubbles may disappear without a trace).
Treatment of blepharitis of the eye
Treatment of blepharitis in children depends on the clinical variant of the disease.
In the treatment of a simple form of the disease, physiotherapeutic methods are used, for example, electrophoresis with solutions of antibacterial drugs or irradiation with UV rays. Systemic vitamin therapy and a hypoallergenic diet are prescribed.
Several times a day, the edges of the eyelids are treated with brilliant green or chamomile decoction, and then an antibacterial ointment (for example, tetracycline) is applied. In cases where ulcerative blepharitis occurs, before applying the ointment, the crusts are softened with sterile petroleum jelly or lanolin and removed.
For demodectic blepharitis, in addition to the above remedies, zinc-ichthyol ointment, alkaline drops, and also treatment of the facial skin with tar soap are used.
Treatment of chronic forms is difficult. It is recommended to continue therapy for a month after symptoms disappear. Local and internal treatment, including the fight against concomitant infections.
Meibomian blepharitis is treated with the methods described above. In addition, the eyelids are massaged (a glass rod is used for this) followed by smearing them with brilliant green.
This article has been read 7,791 times.
Blepharitis symptoms and treatment
IN childhood many children suffer various eye diseases , which can lead to deterioration of vision (conjunctivitis, stye , blepharitis of the eye). Today we will tell you about what types of blepharitis most common in childhood, symptoms, characteristic of one or another type of blepharitis and treatment diseases using modern and folk remedies.
Blepharitis is called inflammatory process on the edges of the eyelids, which is often chronic and occurs quite often in children. In most cases the appearance of the disease is provoked by Staphylococcus aureus. Cure such eye inflammation in a child difficult, but Lately developed effective methods treatment and complete destruction of the infection that causes inflammation of the eyes ( drops , ointments, special compresses for the eyes).
Blepharitis in children Symptoms, which appear first.
Signs of blepharitis in children include swelling and swelling of the eyelids, excessive loss of eyelashes , redness of the eyes, which is accompanied by itching and burning. There is noticeable irritation under the lower eyelid, as if dirt had gotten there.
Seborrhea, or scaly blepharitis of the eye (photo below)- a disease that is characterized by narrowing of the palpebral fissure, burning in the eyes, the eyelids turn red and become thicker. However, the patient tolerates this type of illness much easier than ulcerative blepharitis. Schoolchildren are the main contingent that faces with ulcerative blepharitis. Crusts form near the eyelashes on the edges of the eyelids, ulcers appear under them, and they bleed from time to time. Angular blepharitis received this name due to the fact that it affects only the corners of the palpebral fissure. For meibomian blepharitis In the eyes, the meibomian glands become inflamed (they are located in the cartilage tissue of the eyelids). When you press on the eyelid, a white mass with a yellow tint begins to flow out.
Blepharitis in children Treatment and disease prevention.
If blepharitis occurs after an eye infection, the child is prescribed antibiotics. When the cause of the disease is an allergy , then you need to stop the access of the allergen to the eye, rinse the baby’s eyelids warm water with soap, stop irritating the surface with ambrosia (if there was a reaction to it).
In advanced situations, peeling is observed skin around the eyes and eyebrows, on the head. Then the doctor recommends using a specialized cream or shampoo.
Another type of disease is demodectic blepharitis, named after its pathogen - the Demodex mite. Demodex lives in the bulb of the eyelash, and gets there when a child comes into contact with birds, their down and feathers that fill pillows. Increased likelihood catch the disease in children with chronic gastrointestinal problems, diabetes, various types of allergies , focal points of infection. When mite begins life activity in the follicles of the eyelashes, the epithelium peels off and these cells accumulate between the hairs. Cylindrical muffs form near the roots of the eyelashes; they become larger over time.
Treat demadecosis blepharitis problematic: the marginal edge, the skin of the eyelids and face have to be treated with alcohol solutions.
Often blepharitis in children (see photo below) develops due to weakened immunity, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, constant eye strain ,diabetes mellitus or the presence of worms. Therefore, if you notice symptoms of blepharitis in your child, it is important to immediately seek help. professional help To pediatrician to identify the causes and source of the disease, the passage necessary examination and analyses. If a child is diagnosed blepharitis, treatment will be aimed at strengthening immune system child, adjusting the diet and regularly taking medications (as well as using ointments and special lotions, shampoos) until the infection is completely eliminated and eliminating the symptoms of blepharitis.
Now you know what symptoms indicates that the child is developing blepharitis eye. We looked at the types of blepharitis, treatment methods diseases and methods prevention of re-infection (development chronic blepharitis). We also learned that demodectic blepharitis is caused by a mite that penetrates the eyelash bulbs and causes eye inflammation in a child.
Next article.
If your child has blepharitis, their eyelids may become irritated, red, scaly, and swollen. When your child wakes up in the morning, you may notice a crust forming on his eyelids. The child may feel a burning and itching sensation on the eyelid, and when blinking, he may have the feeling that something is in the eye. Children with blepharitis may also experience excessive tearing.
Causes of blepharitis in children
Blepharitis occurs when excess sebum on the edges of the eyelids causes an overgrowth of bacteria that reside on the eyelids. As a result, the edges of the eyelids become irritated and inflamed.
Blepharitis often occurs along with seborrheic dermatitis (dry patches of flaky, scaly skin on the scalp or face), allergies, or rosacea (a skin condition that causes redness on the face).
Should I take my child to the doctor?
You will need to take your child to a doctor to have his eyes examined. While adults can try to treat this disease on their own before seeing a doctor, it is better to take your child to the doctor to make sure that you are dealing with blepharitis, and then begin immediate treatment.
Chronic condition and relapses of blepharitis in children
Blepharitis is treatable, but relapses of the disease can occur. Unfortunately, this disease is often chronic.
Blepharitis can begin in infancy and can go away and recur over many years. Maintaining good eyelid hygiene is important preventive measure for a child who once had blepharitis. With appropriate treatment and good hygiene, you can reduce the number of flare-ups.
Blepharitis in a child - the upper and lower eyelids are very swollenTreatment of blepharitis in children
You will likely be advised to apply warm compresses to your child's eyelids for 5 to 10 minutes, 2 to 4 times a day (replace the lotion each time it cools). After applying compresses, gently massage your eyelids in a circular motion with a clean fingertip or warm cloth.
If your child is old enough to follow simple instructions, ask him to look up when you clean his lower eyelid and down when you clean his upper eyelid. To clean the eyelids, use a cotton or gauze swab, or a clean tissue, gently wiping away any particles along the eyelid.
If a child has a blepharitis-related condition, such as dermatitis or rosacea, they must be treated at the same time.
Inflammation of a child's eye is a problem that many parents face. Often mothers are interested in what causes inflammation, what treatment should be used and whether it is possible to treat the baby at home. Inflammation of the eye is a fairly common disease today. It is observed in newborns and older children and has pronounced symptoms. Treatment can be carried out at home, but not for infants. Infants should be treated under specialist supervision.
The most common eye disease in adult children and newborns is conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye). Children of all ages can be affected by conjunctivitis.
When a child's eyes become inflamed, the eyelids become swollen, blood vessels stand out, the eyes turn red and take on a painful appearance.
The eye is an organ consisting of different tissues and particles that perform a variety of tasks. By the definition of eye inflammation, we mean a variety of inflammatory processes. Various inflammations affect the constituent parts of the eye. For example, inflammation of the eyeball itself is noticeable by the redness of the connective tissues of the organ. Inflammatory processes also affect the areas around the eye - the eyelids, which causes discomfort and discomfort.
Century
Inflammation of the eyelid is caused by diseases such as: blepharitis, barley, molluscum contagiosum, abscess, boil.
Barley
Barley is an inflammation in the tissues of the eyelid, which occurs due to the penetration of bacteria - staphylococcus sebaceous gland. Symptoms when you have a cold. Obvious symptoms are swelling near the lower eyelid. Furuncle - inflamed tissue with purulent contents. The boil opens on its own, all the contents come out, and after a while a small scar forms.
Blepharitis is characterized by prolonged inflammation of the eyelids. Localized at the lower end of the eyelid. With blepharitis, the eyelids become swollen and heavy. Eyes itch and burn. The abscess is characterized strong process suppuration, develops after a boil disease.
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the conjunctiva or mucous membrane of the eye is the most common inflammatory disease of the eye. Occurs due to the influence of chemical, physical and bacterial factors. Conjunctivitis often occurs after a foreign body enters the mucous membrane, resulting in inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye. Inflamed spider veins covers the white of the eye and internal sides century.
It often affects both eyes at once. First one eye becomes inflamed, and after a few days the second. Conjunctivitis is not considered a very serious disease, but it brings a feeling of discomfort and irritates the mucous membrane. There are 3 types of conjunctivitis: allergic, bacterial, viral.
Allergic
An allergic form of eye inflammation is formed as a result of an allergic reaction of the body. Allergies are caused by foods medical drugs, house dust, pollen from flowers. With this form, the eyelids turn red and pus is released. Allergic conjunctivitis irritates the nasal cavity in addition to the eyes. This type of conjunctivitis is easy to treat; the symptoms will disappear on their own when you remove the cause of the allergy.

Bacterial
The bacterial form affects two eyes at once. Mainly due to the penetration of dirt and sand into the baby's eyes. Foreign bodies injure the mucous membrane, bacteria gain access to the deep layers of eye tissue, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Viral
The viral form is formed during a cold or sore throat. The disease is transmitted from one eye to the other. The baby feels discomfort in the eye, cutting sensations, burning, itching. The mucous membrane becomes red, purulent discharge is observed.
Tear ducts
Inflammation in the lacrimal canals of the eye mainly occurs in children due to dacryocystitis, canaliculitis, and dacryoadenitis.
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is a purulent process that is located on the wall of the lacrimal sac. It is characterized by swelling and redness of the skin over the lacrimal sac. Often observed in newborns.
Canaliculitis
Canaliculitis – manifested by inflammation of the lacrimal ducts. Develops as complications of conjunctivitis or dacryocystitis. During the disease there is copious discharge tears.
Dacryodenitis
Dacryodenitis - inflammation of the lacrimal gland, occurs during complications of infectious diseases (colds, flu, sore throat, measles). With dacryodenitis, the head hurts, the temperature rises, and there is a loss of strength.
Choroid
Inflammation of the choroid or iris is called iritis and iridocyclitis. Iritis affects the iris itself, and cyclitis affects the ciliary body. Inflammation occurs due to sinusitis, traumatic eye injuries, and dental pathology.
In newborns
Very often, eye inflammation occurs in a newborn baby. The children are still quite weak and are just beginning to get used to their new environment. When symptoms of inflammation appear, you should consult your doctor to prescribe correct treatment for a small patient.

Inflammation of the eye in newborns is noted due to dacryocystitis. Occurs due to underdevelopment of the tear ducts. Blepharitis is also observed in newborns. The baby's eyelids become inflamed and eyelashes fall out. The causes of eye inflammation are various infectious diseases, poor living conditions, and hypovitaminosis. For additional diagnostics, the newborn is examined for worms.
Blennorea
Blenorrhea of newborns is an inflammation of the eyes that is common. When a baby is born, you should immediately wipe your eyelids with sterile materials. Then drop 1 drop of 1% lapis solution into both eyes. The therapy helps protect the newborn from bacteria from the mother’s genitals. Blenorrhea in newborns is accompanied by swelling, redness of the eyelids, and the release of sticky contents.
Eye inflammation in a newborn occurs due to conjunctivitis. The cause of the disease may be swimming in unsterile water or contact with objects used by an infected person. The body of newborns is quite weak and catches various viruses.

Symptoms
Inflammation of the eye in a child is determined general symptoms, which are similar in almost all diseases. The main symptoms of inflammatory eye diseases:
- redness of the eye;
- strong lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- copious discharge from the eye;
- burning and itching;
- presence of pus;
- photosensitivity;
- painful sensations;
- discomfort;
- increased body temperature;
- blurred vision.
If you find any of the listed symptoms, you should consult an ophthalmologist to establish an accurate diagnosis. Treatment should begin immediately.
Treatment
Treatment must begin with eliminating the cause of the disease. You should not make a diagnosis yourself; you need to consult a specialist. You should make an appointment with a doctor if you notice any symptoms.
Drops
Eye drops are considered the most effective method against inflammation. You need to choose drops depending on the reasons that caused the inflammation. Eg, with a cold or exposure bacterial infection, antibiotic drops are prescribed. If the baby’s tear ducts are disrupted, then you need to use drops that are similar in composition to human tears.

- Treatment of conjunctivitis is accompanied by the use of drops that have an antibacterial effect: Levomycetin, Sulfacyl sodium.
- Eye drops for inflammation of the eyelid are used for diseases such as: blepharitis, boils, abscess, molluscum contagiosum. Prescribed drops: Penicillin, Erythromycin solution.
- When the functioning of the lacrimal organs is disrupted, drops are prescribed: Licontin, Oftolik, Oksial, Visomitin. To relieve inflammation that causes allergies, use: Visin, Naphthyzin.
To apply eye drops, the newborn must be swaddled and placed on a flat surface. Both eyes need to be instilled, as inflammation passes from one eye to the other.
Folk remedies
There are good folk remedies for treating eye inflammation in children. As a rule, these are compresses and rinses. It is important to consult a doctor before starting treatment and using folk remedies.
Compresses
Compresses relieve irritation and soothe the skin. Compresses made from tea, parsley, and various herbs help well.
- To prepare parsley compresses you need: finely chop the parsley, wrap it in gauze and dip in boiling water. As soon as all the water has drained and the gauze has cooled, it should be applied to eyes closed for a few minutes.
- Recommended for eye inflammation tea compresses. The tea should be brewed, cooled, and allowed to brew for about 30 minutes. Then strain and apply on eyes for 10 minutes.
- Compresses from jasmine leaves, rose hips and clover removes inflammation well. Pour boiling water over all ingredients, add a little honey, leave for 20 minutes, and strain. The compresses are ready.
- You can infuse compresses in boiled milk. Compound: leaves of rose, burdock, calendula. Leave on a warm heating pad for 7 minutes. Apply warm to eyes.

Washing
Effective rinsing folk remedy. You can wash your eyes with infusion pharmaceutical chamomile. For 1 glass of hot water 4 tbsp. spoons of chamomile. Leave for about an hour. Wash eyes with decoction onions. To do this, boil the onion, add a little honey to the broth and boric acid. You need to rinse about five times a day.
It is forbidden to wash the baby's eyes with mother's milk and saliva. Milk and saliva are a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria.
Today, blepharitis in children is frequent illness. This is an inflammation of the edges of the eyelids associated with too much thin layer in this place of the skin and fiber, due to the looseness of tissues and complete absence fat
In some cases the eye for a long time may remain without visible changes, although blepharitis will develop in full swing. This gives parents the erroneous opinion that this disease is quite simple and does not require any special drug treatment. In fact, inaction with such a diagnosis can result in serious complications for the child’s health. To avoid them, you need to try to protect your baby from factors that provoke the development of childhood blepharitis.
Causes
- past infectious diseases;
- severe fatigue (both physical and mental);
- hypothermia;
- demodex mite, which gets into the eyelash bulbs when the baby comes into contact with birds, down and feather pillows, as well as in chronic gastrointestinal problems, diabetes, different types allergies, focal points of infection;
- weakened immune system;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, gastritis, cholecystitis);
- constant visual tension;
- diabetes;
- dirt getting under the eyelids;
- sensitivity to various irritants (pollen, cosmetics, dust);
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- bleeding from a sore tooth, tonsils;
- refusal to wear glasses if you are farsighted, as the eye muscles suffer from tension and fatigue;
- avitaminosis;
- rubbing the eyes with dirty hands;
- external atmospheric phenomena: exposure to wind, smoke, dust.
If parents know exactly what causes can cause such an unpleasant disease in a child as blepharitis, they can somehow protect the eyes from infection. First, teach him to follow basic hygiene rules. Secondly, introduce him with early years To healthy image life. Thirdly, treat any internal diseases. If it was not possible to protect the baby, you need to see the first signs of blepharitis in a timely manner. This will allow treatment to begin as early as possible.
Symptoms and signs

The complexity of this disease is that the symptoms of blepharitis in a child are easily confused with signs of other eye diseases. The same barley, for example. Therefore, if abnormal, unhealthy phenomena occur in the baby’s eyes over a certain period of time, parents should seek help from a doctor as soon as possible. These symptoms may include:
- swelling, swelling of the eyelids;
- redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes;
- sticking and loss of eyelashes;
- burning;
- hyperemia;
- irritation under the lower eyelid;
- narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- thickening of the eyelids;
- crusts along the edges of the eyelashes, which then turn into bleeding ulcers;
- if there is inflammation of the meibomian glands, when pressure is applied to the eyelids, a whitish mass of a yellowish tint flows out from under them;
- feeling of discomfort in the eye area;
- peeling of the skin on the head, around the eyebrows and eyes;
- telangiectasia - visible dilation of small blood vessels of the skin in the form of a mesh or stars.
If there are several such manifestations, it is recommended to show the child to a doctor as soon as possible and not self-medicate. Symptoms of blepharitis are a signal that specialist intervention is required. Only he will be able to conduct a competent diagnosis and prescribe therapy in accordance with the type of disease.
Types of blepharitis
In medicine, there are several types of childhood blepharitis (depending on its symptoms and origin):
- scaly (simple, seborrhea);
- ulcerative;
- angular;
- meibomian;
- demodectic;
- allergic;
- chronic;
- Rosacea.
Any of these types of blepharitis in children is characterized by its own characteristics, on which the prescribed treatment will depend.
Treatment of the disease
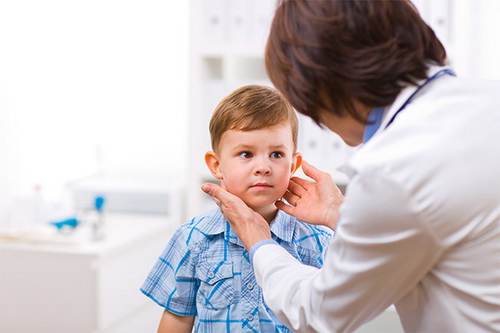
After the doctor examines the child, conducts an examination, talks with the parents, and identifies possible reasons diseases, diagnose the symptoms, determine the type of blepharitis in the child, he will give recommendations on how to treat it.
- When allergic blepharitis is diagnosed in children, it is recommended to avoid contact with the allergen and wash the eyelids with warm, filtered water and soap.
- Special eye cream.
- Shampoo if blepharitis is seborrheic and has touched the scalp.
- Treatment of the edges of the cilia with an alcohol solution may be prescribed for demodectic blepharitis.
- Strengthening the immune system with vitamin therapy.
- Adjustment of diet, hypoallergenic diet.
- Massage of the century.
- Physiotherapeutic methods such as electrophoresis with medicinal solutions (antibiotics, vitamins C and B are most often prescribed), UHF therapy, UV irradiation, magnetic therapy, darsonvalization.
- External treatment of the eyelids with a 70% solution of ethyl alcohol, 1% brilliant green, tincture of medicinal calendula, decoction of chamomile.
- External treatment of eyelids affected by blepharitis with antibacterial ointments: erythromycin, tetracycline, Oriprim-P, Colbiocin, Ophthalmotrim.
- Combined ointments medications, combining both an antibiotic and glucocorticosteroids: Maxitrol, Dex-gentamicin, Garazon.
- When treating ulcerative blepharitis in children, it is recommended to carefully remove purulent crusts from the eyelids. They can be easily removed if you soften them first with lanolin or sterile petroleum jelly.
- Antimicrobial eye drops instilled into the conjunctival sac: solutions of miramistin, picloxidine, sodium sulfacyl, chloramphenicol.
Prescribed by a doctor timely treatment Blepharitis in children leads to complete recovery without complications. If you miss the disease initial stage and ignore medication assistance, this can lead to the most undesirable consequences up to deterioration of vision.
